

Heads up: Our content is reader-supported. This page includes affiliate links. If you click and purchase, I may receive a small commission at no extra cost to you.
When you choose a web hosting provider, you’re essentially renting a piece of their physical server to store your website’s data. This server is connected to the internet and is constantly available to receive requests from visitors. When someone types in your website’s address, their browser sends a request to your server, which then sends back the files that make up your website.
The cost of web hosting varies depending on the provider and the type of hosting plan you choose. Shared hosting is the most affordable option, but it also means sharing the resources of a server with other websites. VPS hosting is more expensive, but it gives you more resources and more control over your server environment. Dedicated hosting is the most expensive option, but it gives you complete control over a physical server.
No matter which type of web hosting you choose, it’s important to make sure that the provider you choose is reliable and has a good reputation. You should also make sure that the provider offers the features and support that you need for your website.
What is a web hosting service?
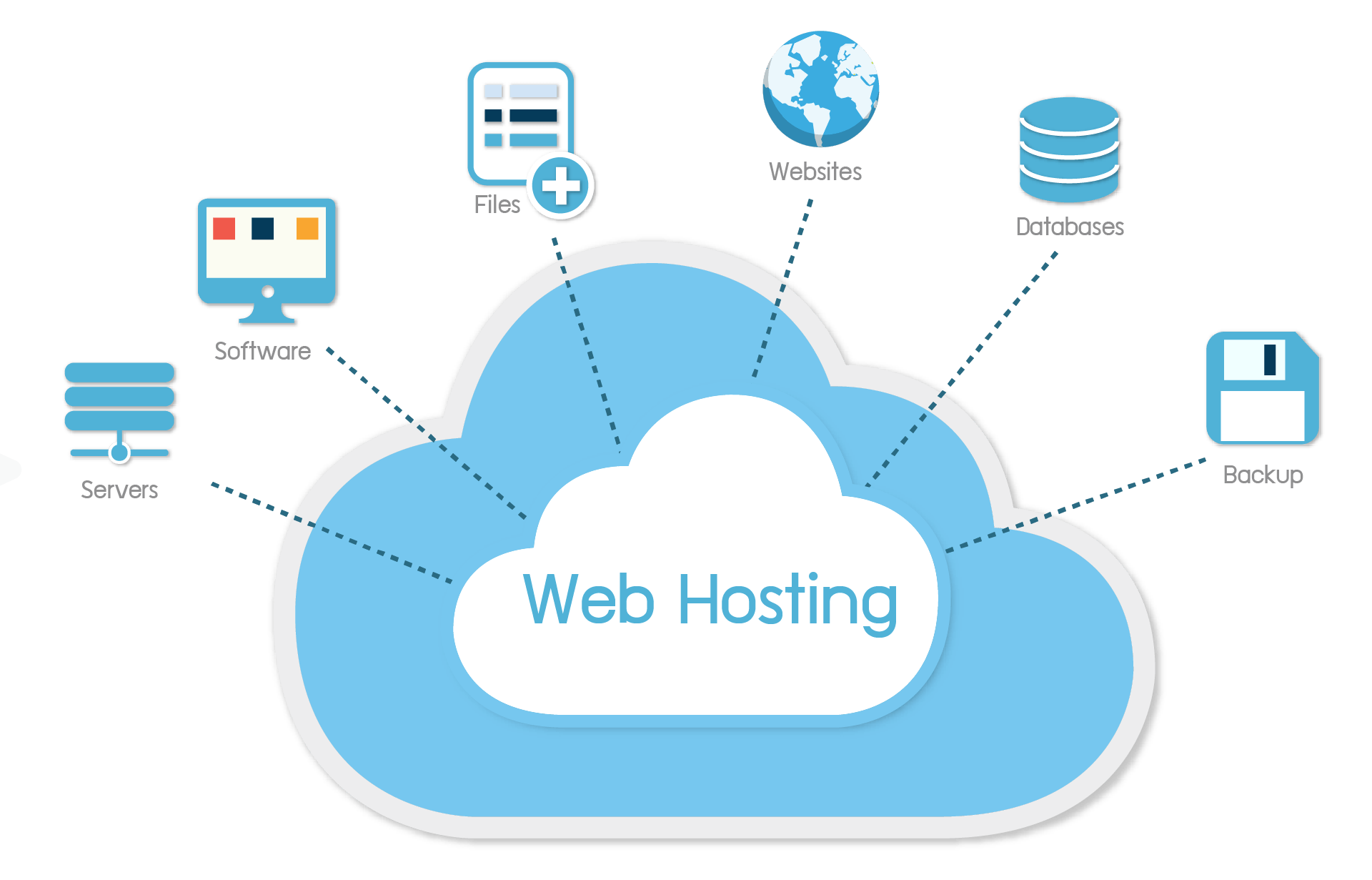
Web hosting is a service that allows individuals and organizations to make their websites accessible on the internet. Hosting providers allocate space on servers, which are powerful computers connected to a high-speed network. These servers store website files, making them accessible to users worldwide. Web hosting services enable individuals, businesses, and entities to establish an online presence and share their content with a global audience.
When a user types a website address (URL) into a web browser, the browser sends a request to the hosting server where the website is stored. The server then retrieves the requested files and displays the website’s content in the user’s browser. This process happens seamlessly, allowing users to access websites quickly and efficiently.
Here are the key aspects and functionalities of a web hosting service:
Server Storage and Resources:
A web hosting service provides server space where website files, databases, and other essential elements are stored. This server space is equipped with the necessary computing resources such as processing power, memory (RAM), and storage capacity.
Connectivity and Bandwidth:
Web hosting services ensure that websites are connected to the internet with high-speed and reliable connectivity. Bandwidth, often measured in gigabytes per month, represents the amount of data that can be transferred between the server and users accessing the website.
Domain Hosting:

Web hosting services often include domain hosting, allowing users to associate their websites with a unique domain name (e.g., www.yourwebsite.com). This involves configuring domain settings to point to the server where the website is hosted.
Types of Web Hosting:
Various types of web hosting services cater to different needs. These include Shared Hosting (multiple websites sharing resources on a single server), Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting (virtual partitions within a server for more control), Dedicated Hosting (an entire server dedicated to a single user), and Cloud Hosting (resources distributed across multiple servers for scalability).
Control Panel:
Web hosting services often provide a control panel interface (e.g., cPanel, Plesk) that allows users to manage various aspects of their hosting account. Users can configure settings, upload files, create email accounts, and perform other administrative tasks through the control panel.
Email Hosting:

Many web hosting services offer email hosting, allowing users to create and manage email accounts associated with their domain (e.g., [email protected]). Email hosting may include features like spam filtering, autoresponders, and webmail interfaces.
Security Measures:
Web hosting services implement security measures to protect hosted websites from potential threats. This includes firewalls, secure socket layer (SSL) certificates for encrypted data transmission, regular security updates, and sometimes malware scanning.
Backup and Recovery:
Regular backups of website data are crucial for safeguarding against data loss. Web hosting services often provide backup solutions, enabling users to restore their websites to a previous state in case of accidental data loss or corruption.
Technical Support:
Reliable customer support is a vital aspect of web hosting services. Users may encounter technical issues or have questions related to their hosting account, and responsive customer support can provide assistance through various channels like live chat, email, or phone.
Scalability:
As websites grow in traffic and content, scalability becomes important. Some web hosting services offer scalability features, allowing users to easily upgrade their hosting plans or access additional resources to accommodate increased demand.
Server Uptime and Reliability:
Server uptime refers to the duration during which a server is operational and accessible. A reputable web hosting service strives for high server uptime to ensure that websites are consistently available to users.
How many Types of web hosting services?
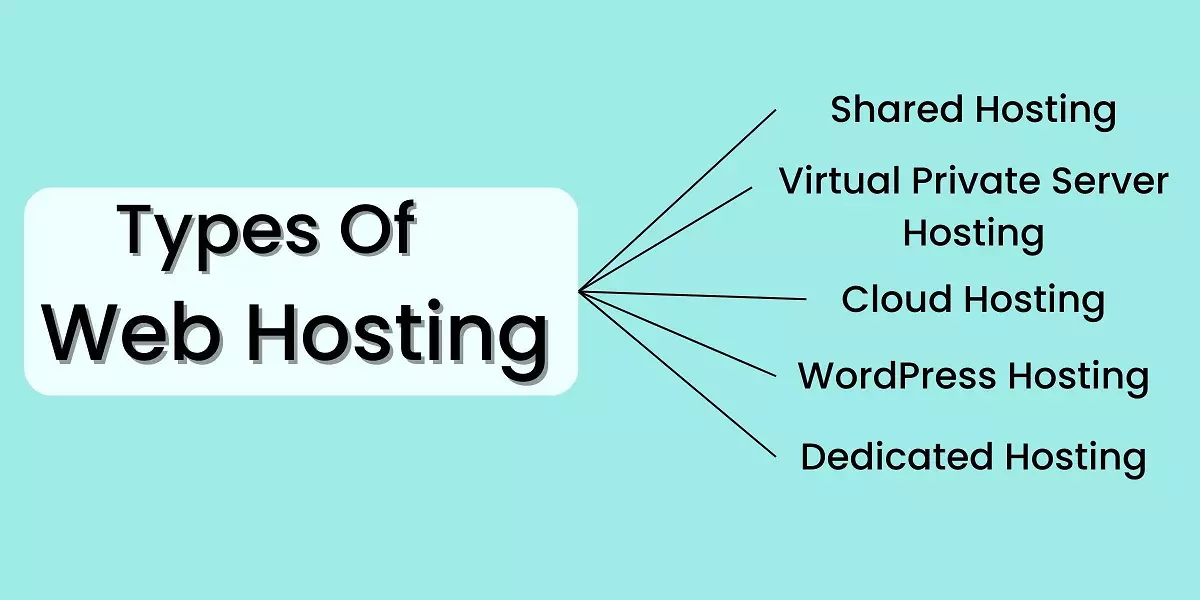
There are several types of web hosting services available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types of web hosting include:
Shared Hosting:
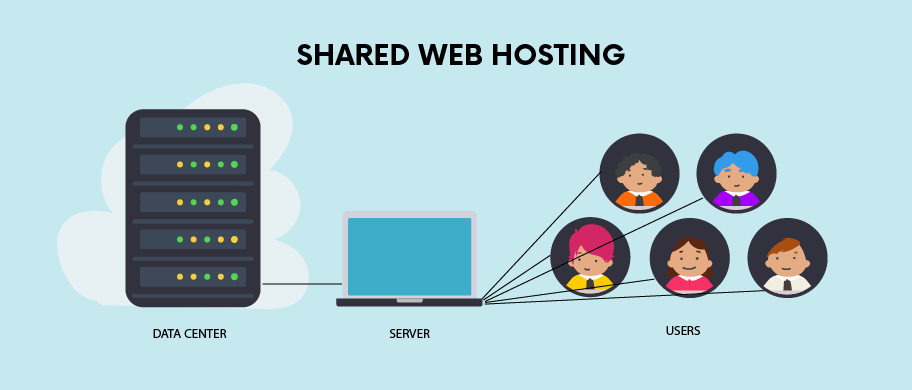
- Multiple websites share resources on a single server.
- Cost-effective for small websites with moderate traffic.
- Resources (CPU, RAM, storage) are shared among multiple users.
Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting:

- A virtual server created by partitioning a physical server.
- Provides more control and dedicated resources compared to Shared Hosting.
- Suitable for websites with higher resource demands.
Dedicated Hosting:
- An entire physical server is dedicated to a single user.
- Offers maximum control over server configurations.
- Ideal for large websites with high traffic and resource-intensive applications.
Cloud Hosting:

- Resources are distributed across multiple virtual servers.
- Provides scalability and flexibility to handle varying workloads.
- Users pay for the resources they consume.
WordPress Hosting:

- Optimized specifically for hosting WordPress websites.
- May include features like automatic WordPress updates and specialized support.
- Suitable for individuals and businesses using the WordPress platform.
Reseller Hosting:
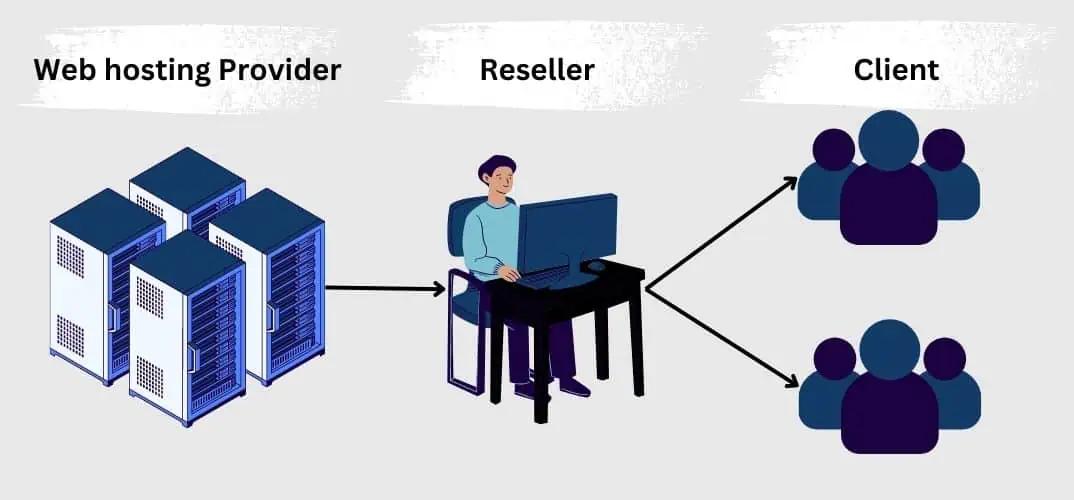
- Users can resell hosting services to their clients.
- Allows individuals or businesses to become their own hosting providers.
- Resources are allocated to the reseller account, who can then distribute them among clients.
Managed Hosting:

- Hosting provider manages technical aspects of server maintenance.
- Ideal for users who want to focus on content and business rather than server management.
- Commonly used for applications like eCommerce or content management systems.
Colocation Hosting:
- Users own their physical server, and the hosting provider provides the infrastructure and connectivity.
- Users have full control over the server hardware and software.
- Requires technical expertise for server maintenance.
Clustered Hosting:
- Multiple servers work together to host a website.
- Enhances reliability and performance by distributing the load.
- Commonly used for large websites with high traffic.
Free Hosting:
- Hosting service provided at no cost.
- Limited resources and features.
- Suitable for personal projects or small websites with minimal traffic.
E-commerce Hosting:

- Optimized for hosting online stores and eCommerce websites.
- Includes features like secure payment gateways and SSL certificates.
- Ensures high performance for handling transactions.
Forum Hosting:
- Designed specifically for hosting online forums and discussion boards.
- Supports features necessary for forum management and user interaction.
- Optimized for handling concurrent user interactions.
What is Shared hosting?
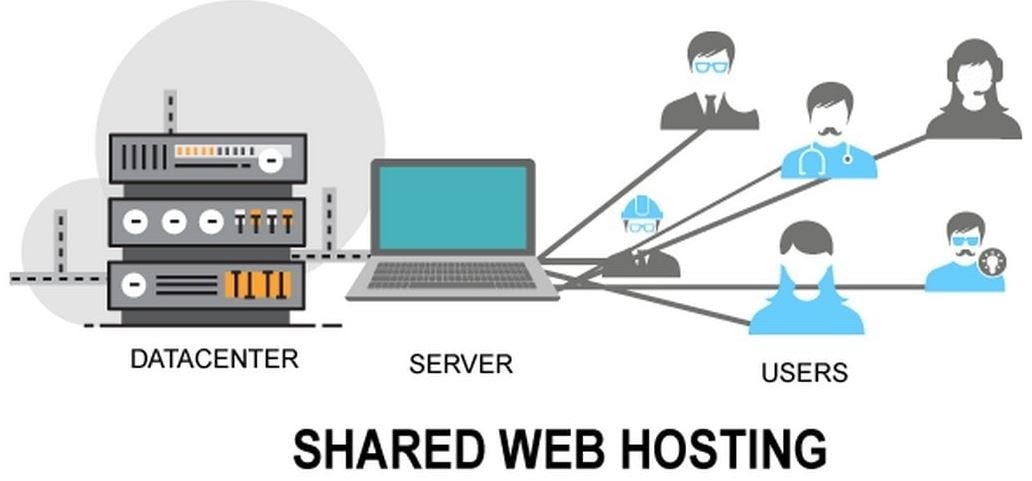
Shared hosting is the most affordable type of web hosting. This is because you share a server with other websites, which means that you are all using the same resources. This can sometimes lead to performance issues, especially if your website is experiencing a lot of traffic. However, shared hosting is a good option for small websites that do not have a lot of traffic or that do not require a lot of resources.
How does Shared Hosting Works?
In shared hosting, multiple websites reside on the same physical server. Each website has its own set of files and data, but they share the server’s resources, such as CPU, RAM, and disk space. This means that when one website experiences a surge in traffic, it can impact the performance of other websites on the same server.
Server Partitioning
To prevent one website from monopolizing server resources, shared hosting providers divide the server into partitions. Each partition acts as a virtual server, and each website is assigned to a specific partition. This ensures that each website has a dedicated amount of resources and that no one website can overwhelm the server.
Resource Allocation
Shared hosting providers use various algorithms to allocate server resources among different websites. These algorithms take into account factors such as website traffic, CPU usage, and memory consumption. The goal is to distribute resources fairly and ensure that all websites have a chance to perform well.
Overuse and Limitations
While shared hosting providers often advertise unlimited resources, there are always limitations. If a website consistently exceeds its allocated resources, it can impact the performance of other websites on the same server. In such cases, the hosting provider may send warnings or even suspend the website until it reduces its resource consumption.
What are the benefits of shared hosting?
- Affordability: Shared hosting is one of the most affordable types of web hosting, making it an ideal option for individuals, small businesses, and startups that are on a budget. The cost of shared hosting plans typically ranges from a few dollars per month to around $20 per month, depending on the provider and the features offered.
- Easy Setup and Management: Shared hosting is generally easy to set up and manage, even for beginners with limited technical expertise. Most shared hosting providers offer cPanel or Plesk control panels, which provide user-friendly interfaces for managing your website files, databases, email accounts, and other settings.
- Scalability: Shared hosting plans can be scaled up or down as your website’s needs grow. If your website experiences a sudden surge in traffic, shared hosting can often handle the increased demand without requiring an immediate upgrade.
- Unlimited Features: Many shared hosting plans offer “unlimited” features, such as unlimited bandwidth, unlimited disk space, and unlimited domains. While there are always practical limitations, these features can provide flexibility and peace of mind for website owners.
- Technical Support: Shared hosting providers typically offer technical support to assist their customers with any issues they may encounter. This support can be invaluable for those who are not familiar with web hosting or server administration.
- Wide Availability: Shared hosting is a widely available type of web hosting, with numerous providers offering a variety of plans and features to choose from. This makes it easy to find a shared hosting plan that meets your specific needs and budget.
What are the disadvantages of shared hosting?
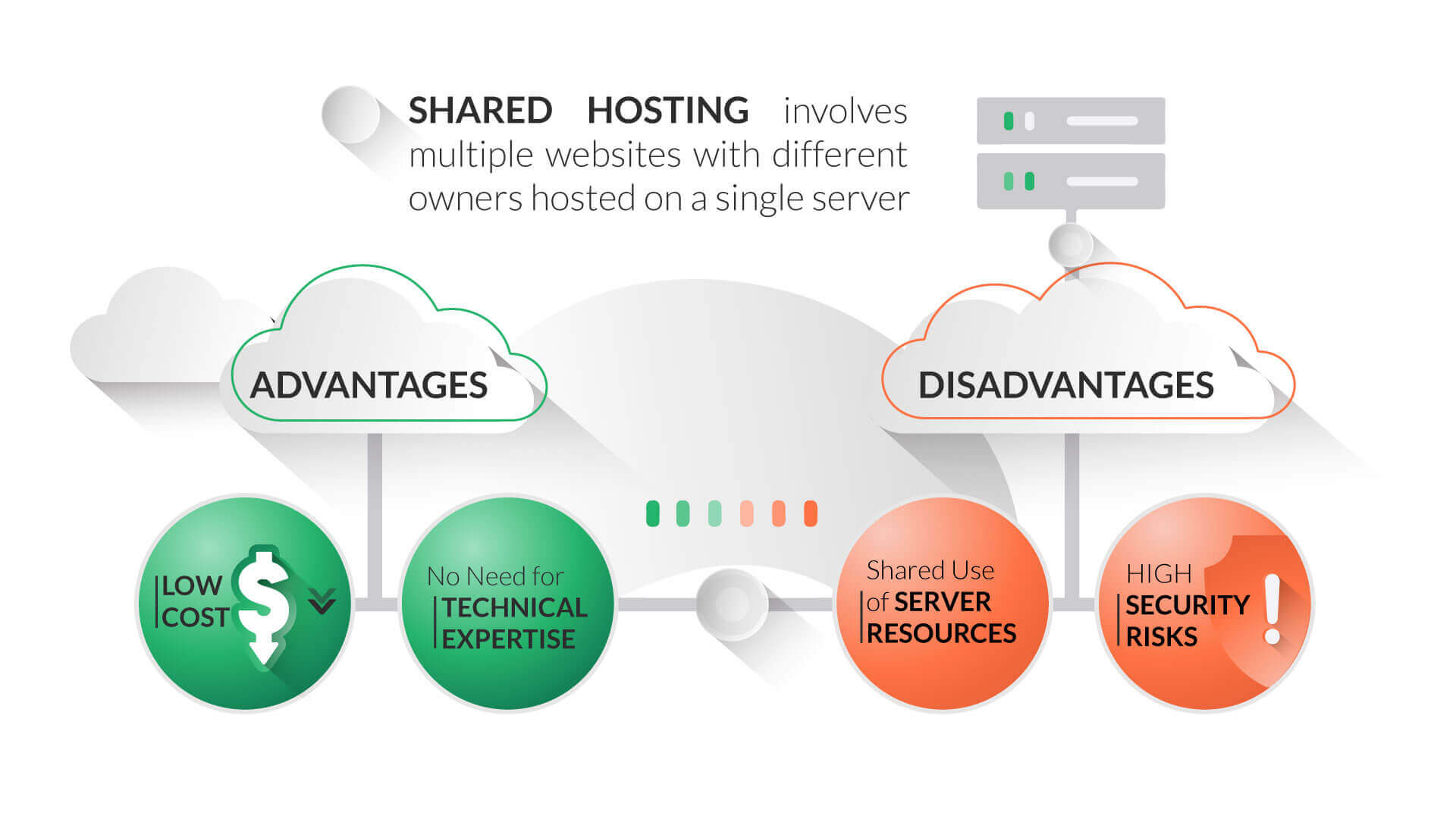
While shared hosting offers several advantages, it also comes with some drawbacks that you should be aware of before making a decision.
- Limited Resources: Shared hosting involves sharing a physical server with multiple websites. This means that the server’s resources, such as CPU, RAM, and disk space, are divided among all the websites on the server. If one website experiences a sudden surge in traffic, it can impact the performance of other websites on the same server.
- Security Concerns: Shared hosting environments can be more vulnerable to security threats. If one website on the server is compromised, it can potentially expose other websites to security risks.
- Limited Customization: Shared hosting plans typically offer limited customization options. You may not have full control over the server configuration, which can restrict your ability to optimize your website’s performance or install specific software.
- Scalability Limitations: While shared hosting can be scaled up to a certain extent, there may come a point where your website’s needs exceed the capabilities of a shared hosting plan. In such cases, you may need to upgrade to a VPS or dedicated hosting plan to accommodate your growing website.
- Potential for Downtime: Shared hosting servers are more susceptible to downtime if there are hardware failures or software issues. If the server goes down, all the websites hosted on that server will be unavailable.
- Reliance on Other Websites: You may experience performance slowdowns or security issues if other websites on the shared server are experiencing high traffic or have poor security practices.
- Limited Control over Server Environment: Shared hosting providers typically have strict policies regarding what you can install or configure on the server. This can limit your flexibility to customize your website’s environment.
- Potential for Suspension or Termination: If your website consistently exceeds the shared hosting plan’s limits or violates the provider’s terms of service, your account may be suspended or terminated.
- Limited Support for High-Traffic Websites: Shared hosting plans are not well-suited for websites that experience high traffic or require specialized features.
- May Not Be Ideal for Sensitive Data: Shared hosting may not be the best option for websites that handle sensitive data or require stringent security measures.
Who might need a shared hosting?
Shared web hosting is an ideal choice for novice webmasters venturing into the realm of web hosting. If you seek an economical solution to launch your websites, shared web hosting might be the perfect fit for you. However, if you intend to manage multiple websites or a single site with substantial traffic, you might want to consider a more comprehensive hosting plan, such as VPS or dedicated hosting.
How do I choose a shared web hosting provider?
There are many shared web hosting providers to choose from. When choosing a provider, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Your budget: How much are you willing to spend on web hosting?
- Your website’s needs: How much traffic does your website expect to receive? What features do you need?
- The provider’s reputation: Read reviews of the provider to learn about their uptime, customer support, and other factors.
Why should I choose Shared Hosting?
To begin with, Shared Hosting stands out for its cost-effectiveness, making it the most budget-friendly option for hosting a website.
When launching a new website, the initial phase usually involves building an audience and adding content gradually. During this early stage, your website is likely to be lightweight, requiring minimal resources. Shared Hosting proves to be the ideal hosting solution in such scenarios, offering affordability, speed, and reliability. Moreover, the scalability of Shared Hosting plans is a seamless process, often taking just a few minutes with reputable hosting providers. As your website and audience expand, transitioning to more robust hosting options becomes a viable and straightforward progression.
How is Shared Hosting different from other forms of hosting?
Dedicated Hosting involves allocating all server resources exclusively to a single website, making it a costly choice primarily utilized by large-scale websites with substantial traffic.
Shared Hosting is often juxtaposed with VPS (Virtual Private Hosting). In both hosting forms, multiple websites share the resources of a single server, yet a crucial distinction separates them.
In VPS, each website receives a predetermined allocation of server resources. For instance, if you opt for a VPS plan with 4GB RAM, 4 CPU cores, and 100GB storage, these resources are exclusively reserved for your use and not shared with any other website. In Shared Hosting, such resource isolation does not exist.
Is Shared Hosting suitable for my website?
Shared Hosting is ideal for small to medium-sized websites, blogs, and businesses with moderate traffic. It may not be suitable for high-traffic or resource-intensive websites, which might benefit more from VPS or Dedicated Hosting.
Whether Shared Hosting is suitable for your website depends on various factors related to your website’s requirements, characteristics, and your specific needs.
Here are some considerations to help you determine if Shared Hosting is a good fit for your website:
Traffic Volume:
- Shared Hosting is generally suitable for websites with moderate to low traffic.
- If your website is expected to receive a substantial amount of traffic, you might want to consider hosting
- options with more dedicated resources, such as VPS or Dedicated Hosting.
Budget Constraints:
- Shared Hosting is cost-effective and often the most affordable option.
- If you have budget constraints and are running a small to medium-sized website, Shared Hosting can be a
- practical choice.
Resource Requirements:
- Shared Hosting allocates resources (CPU, RAM, storage) among multiple users on the same server.
- If your website requires significant resources or has specific performance needs, you might consider hosting
- plans with dedicated resources like VPS or Dedicated Hosting.
Ease of Use:
- Shared Hosting is known for its simplicity and user-friendly interfaces.
- If you are a beginner or do not have advanced technical skills, Shared Hosting is a convenient option as the
- hosting provider manages most server-related tasks.
Website Type:
- Shared Hosting is suitable for various types of websites, including blogs, small business websites, and personal portfolios.
- If you have a content-based website without resource-intensive applications, Shared Hosting is likely sufficient.
Server Customization Needs:
- Shared Hosting plans come with predefined server configurations.
- If you require extensive server customization or control over server settings, you might consider a hosting solution like VPS or Dedicated Hosting.
Security Concerns:
- Shared Hosting is secure, but security measures are shared among multiple users on the same server.
- If your website deals with sensitive information or requires advanced security features, you might want to explore hosting options with additional security measures.
Future Scalability:
- Shared Hosting may have limitations in terms of scalability.
- If you anticipate significant growth in your website’s traffic and resource needs, consider a hosting solution that allows easy scalability, such as VPS or Cloud Hosting.
Support Requirements:
- Shared Hosting providers usually offer customer support, but response times can vary.
- If you require quick and dedicated support or have specific technical requirements, evaluate the support services provided by the hosting provider.
Are there any limitations to Shared Hosting?
Shared Hosting may have limitations on resources, as they are shared among multiple users. If one website experiences a surge in traffic, it could potentially impact the performance of other sites on the same server.
Some common limitations associated with Shared Hosting
- Resource Sharing: Resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage are shared among multiple websites on the same server. This can lead to performance issues if other websites on the server experience spikes in traffic or resource usage.
- Performance Impact: Since multiple users share the same server, the performance of your website can be affected if another site on the server experiences high traffic or resource demands.
- Limited Server Customization: Shared Hosting plans often come with pre-configured server settings, limiting the level of customization and control that users have over server configurations.
- Security Concerns: While Shared Hosting providers implement security measures, the shared environment poses potential security risks. If one website on the server is compromised, it could impact others.
- Limited Scalability: Shared Hosting may have limitations in terms of scalability. If your website experiences significant growth and requires more resources, you may need to upgrade to a different hosting solution.
- Software Restrictions: Some Shared Hosting providers may impose restrictions on the types of software, scripts, or applications that can be installed. Certain resource-intensive or specialized applications may not be supported.
- Email Limits: Shared Hosting plans may have limitations on the number of emails that can be sent per hour or per day. This can impact websites with high email activity.
- Server Uptime Dependencies: The uptime of your website is dependent on the server’s overall performance and the hosting provider’s maintenance practices. Shared Hosting may not guarantee the same level of uptime as more premium hosting solutions.
- Traffic Limits: Shared Hosting plans often come with specific bandwidth or traffic limits. Exceeding these limits may result in additional charges or temporary restrictions on your website.
- Limited Control Panel Features: While Shared Hosting plans include a control panel for managing your account, the features may be limited compared to more advanced hosting solutions.
- Not Ideal for Resource-Intensive Applications: Websites with resource-intensive applications, high levels of interactivity, or complex databases may face performance issues on Shared Hosting.
- Geographical Server Location: Users usually do not have control over the geographical location of the server. This can impact website loading times for users in different regions.
Can I upgrade from Shared Hosting in the future?
Yes, most web hosting providers offer the flexibility to upgrade your hosting plan as your website grows and requires more resources. Upgrading from Shared Hosting to a more robust hosting solution is a common practice and can be a seamless process. Here’s a general outline of how the upgrade process typically works:
Evaluate Your Website’s Needs:
Assess the current and anticipated future needs of your website. Consider factors such as increased traffic, resource requirements, and the need for more advanced features.
Check Hosting Provider’s Upgrade Options:
Review the hosting provider’s offerings and check for available upgrade options. Common upgrades include Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting, Dedicated Hosting, or Cloud Hosting.
Contact Customer Support:
Reach out to the hosting provider’s customer support. Most providers have a support team available through live chat, email, or phone. Discuss your requirements and inquire about the upgrade process.
Select the New Hosting Plan:
Choose the hosting plan that best aligns with your website’s needs. This may involve selecting a plan with more resources, dedicated server options, or additional features.
Migration Assistance:
Hosting providers often offer migration assistance to transfer your website from Shared Hosting to the upgraded plan. This may include moving files, databases, and configurations to the new server.
DNS Update:
If you are using a custom domain, you may need to update your domain’s DNS settings to point to the new server. This ensures that visitors are directed to the correct hosting environment.
Testing and Verification:
After the migration is complete, it’s advisable to thoroughly test your website on the new hosting plan. Verify that all functionalities are working as expected and that there are no issues.
Communicate with Stakeholders:
If your website has users, subscribers, or stakeholders, communicate the upgrade to them in advance to minimize any potential disruptions. Inform them of any changes in website URLs or functionality.
Monitor Performance:
Monitor the performance of your website on the new hosting plan. Ensure that it meets your expectations in terms of speed, reliability, and overall functionality.
Adjustments as Needed:
Depending on the nature of your website and any new features or settings offered by the upgraded plan, you may need to make adjustments or optimizations to maximize the benefits of the new hosting environment.
How secure is Shared Hosting?
Shared Hosting is generally secure, but security depends on the hosting provider. It’s essential to choose a reputable provider that implements security measures, such as firewalls and regular backups.
The security of Shared Hosting depends on various factors, including the hosting provider’s practices, the diligence of website owners in implementing security measures, and the shared nature of the hosting environment.
Shared hosting is generally considered to be less secure than other types of web hosting, such as VPS or dedicated hosting. This is because multiple websites share the same physical server, which can make it easier for hackers to compromise one website and then use that access to attack other websites on the server.
Some of the security risks associated with shared hosting
- Cross-site scripting (XSS): XSS is a type of attack that allows attackers to inject malicious code into a website. This code can then be used to steal user information, redirect users to malicious websites, or even take control of the website.
- SQL injection: SQL injection is a type of attack that allows attackers to inject SQL code into a website’s database. This code can then be used to steal user information, delete data, or even take control of the database.
- Malware infections: Malware is malicious software that can be installed on a website without the owner’s knowledge. Malware can be used to steal user information, redirect users to malicious websites, or even take control of the website.
Can I host multiple domains on a Shared Hosting plan?

Yes, you can host multiple domains on a shared hosting plan. This is known as addon domains or multisite hosting. Addon domains allow you to host multiple websites on a single shared hosting account. Each addon domain has its own website files, database, and email accounts.
However, not all shared hosting plans allow you to host multiple domains. Some plans only allow you to host one domain, while others allow you to host a limited number of addon domains. If you need to host multiple domains, you will need to choose a shared hosting plan that offers addon domain support.
How it typically works:
Addon Domains:
Hosting providers that support multiple domains on a Shared Hosting plan usually offer the ability to add additional domains through the control panel.
You can add these domains as “addon domains,” and each addon domain can have its own separate website with its content and settings.
Domain Aliases:
Some hosting providers use the term “domain aliases” to describe the ability to host multiple domains on a single account. These additional domains can point to the same website content as the primary domain or have their own unique content.
Resource Allocation:
While you can host multiple domains on a Shared Hosting plan, it’s important to note that the resources (such as disk space, bandwidth, and processing power) are shared among all hosted domains. This means that the total resource usage is distributed among all the websites on the server.
Configuration and Management:
The configuration and management of addon domains or domain aliases are typically done through the hosting provider’s control panel (e.g., cPanel, Plesk). Users can set up additional domains, manage files, and configure settings for each domain.
DNS Configuration:
When adding a new domain to your Shared Hosting account, you’ll need to configure the domain’s DNS settings to point to the hosting provider’s server. This is usually done through the domain registrar’s control panel.
Subdomains:
Some hosting plans also allow the creation of subdomains for each addon domain. Subdomains are extensions of the primary domain (e.g., blog.yourdomain.com), and they can have their own content.
How does customer support work with Shared Hosting providers?
Customer support plays a crucial role in shared hosting services, as it provides assistance to website owners who may encounter technical difficulties or have questions about their hosting plans. The specific nature of customer support varies among shared hosting providers, but it typically involves several key elements:
- Accessibility: Customer support should be readily accessible through various channels, such as phone, email, live chat, and ticketing systems. This ensures that customers can reach out for help when they need it, regardless of their preferred method of communication.
- Response Time: Shared hosting providers should aim to provide prompt responses to customer inquiries. Timely responses demonstrate the provider’s commitment to resolving issues quickly and efficiently, minimizing downtime and frustration for website owners.
- Knowledge Base and FAQs: Many shared hosting providers offer extensive online resources, such as knowledge bases and FAQs, to empower customers to find answers to common questions and troubleshoot issues independently. This self-service approach can reduce the burden on customer support representatives and provide faster solutions for customers.
- Technical Expertise: Customer support representatives should possess a solid understanding of shared hosting technology and be able to effectively diagnose and resolve technical issues. They should also be able to provide guidance on website optimization, security measures, and other technical aspects of web hosting.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Customer support representatives should be adept at problem-solving and able to identify the root cause of issues, even when they are complex or involve multiple factors. They should also be able to communicate solutions in a clear and concise manner, ensuring that customers understand the steps they need to take.
- Empathy and Professionalism: Customer support representatives should approach interactions with empathy and professionalism, recognizing that website owners may be facing challenges with their online presence. They should listen attentively, provide reassurance, and maintain a positive attitude throughout the support process.
- Follow-Up and Escalation: Customer support representatives should follow up with customers to ensure that their issues have been resolved to their satisfaction. They should also be able to escalate complex issues to higher levels of expertise if necessary.
Are there any tips for optimizing a website on Shared Hosting?

Optimize your website by using efficient coding practices, optimizing images, and utilizing caching. Regularly monitor your website’s performance and consider upgrading your hosting plan if needed.
Some tips for optimizing your website on a Shared Hosting plan
Choose a Reliable Shared Hosting Provider: The foundation of a well-optimized website lies in selecting a reputable shared hosting provider. Look for providers with a strong track record of uptime, positive customer reviews, and adequate resource allocation for shared hosting plans.
Optimize Images and Media: Images and media files can significantly impact page loading times. Compress images using appropriate formats like JPEG or PNG, and resize them to fit their intended display size. For videos, consider using lightweight formats like MP4 or WebM.
Enable Browser Caching: Browser caching stores website elements locally on users’ devices, reducing the need to re-download them on subsequent visits. Enable browser caching to improve page loading times for returning visitors.
Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML: Minification removes unnecessary characters, whitespace, and comments from code files, reducing their size and improving loading times. Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files to optimize website performance.
Leverage Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs distribute website content across multiple servers worldwide, reducing the load on the shared hosting server and speeding up content delivery to users based on their location. Consider using a CDN to enhance global performance.
Enable Gzip Compression: Gzip compression reduces the size of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files by encoding them, making them smaller and faster to transfer. Enable Gzip compression to optimize website loading times.
Implement Lazy Loading: Lazy loading only loads images and videos as a user scrolls down the page, rather than loading everything at once. This technique can significantly improve initial page load times, especially for pages with extensive media content.
Optimize Database Queries: Efficient database queries are crucial for website performance. Review and optimize database queries to minimize their execution time and reduce the load on the shared hosting server.
Keep WordPress Themes and Plugins Updated: Outdated WordPress themes and plugins can introduce performance issues and security vulnerabilities. Regularly update WordPress themes and plugins to ensure optimal performance and security.
Monitor Website Performance: Regularly monitor website performance using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix. These tools provide valuable insights into website performance bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
What is the cost range for Shared Hosting plans?
Shared Hosting is generally affordable, with plans ranging from a few dollars to around $10-20 per month. Prices may vary based on the hosting provider and the features included.
Shared hosting plans typically range from a few dollars per month to around $20 per month, depending on the provider and the features offered.
- Basic shared hosting plans with limited resources and features $3 – $5
- Moderate shared hosting plans with more resources and features $5 – $10
- Advanced shared hosting plans with ample resources and features $10 – $20
The specific cost of a shared hosting plan will also depend on the provider. Some providers offer more affordable plans with limited features, while others offer more expensive plans with more comprehensive features.
Do Shared Hosting plans come with a control panel?
Yes, Shared Hosting plans typically come with a control panel that allows users to manage various aspects of their hosting accounts. A control panel is a web-based interface that simplifies the process of configuring and managing hosting-related settings without the need for extensive technical knowledge. The most commonly used control panels for Shared Hosting include:
cPanel:
cPanel is one of the most widely used control panels in the hosting industry. It provides a user-friendly interface with tools for managing domains, email accounts, databases, file storage, security settings, and more. Many hosting providers offer cPanel as the default control panel for Shared Hosting.
Plesk:
Plesk is another popular control panel that provides a similar set of features to cPanel. It is known for its simplicity and is often used by hosting providers that offer both Linux and Windows hosting solutions. Plesk supports various web hosting technologies and allows users to manage multiple domains.
DirectAdmin:
DirectAdmin is a lightweight and straightforward control panel that offers a range of features for managing hosting accounts. It provides tools for domain management, email configuration, file management, and more. Some hosting providers offer DirectAdmin as an alternative to cPanel.
Custom Control Panels:
Some hosting providers may develop their custom control panels to provide a unique user experience. These custom control panels are designed to offer specific features and functionalities tailored to the provider’s hosting environment.
Control panels make it easier for users to perform various tasks related to website management, including:
- Domain Management: Add, remove, or manage domains associated with the hosting account.
- File Management: Upload, download, and organize website files using a file manager.
- Email Configuration: Create and manage email accounts, set up forwarding, and configure email settings.
- Database Management: Create and manage databases, configure database users, and perform database-related tasks.
- Security Settings: Configure security settings, set up SSL certificates, and manage access controls.
- Website Statistics: Access website statistics, including information on traffic, bandwidth usage, and error logs.
- One-Click Installs: Some control panels include tools for easy installation of popular applications, content management systems (CMS), and scripts.
The specific features and layout of the control panel may vary between hosting providers and the control panel software they use. When choosing a Shared Hosting plan, it’s beneficial to consider the control panel provided, as it greatly influences the user experience and ease of managing your website.
Can I install custom applications or scripts on Shared Hosting?
Yes, you can install custom applications or scripts on shared hosting, but there are some limitations. Shared hosting providers typically have restrictions on what you can install on your server. This is because they need to protect the integrity of their servers and prevent users from installing malicious software that could affect other users on the server.
Some general guidelines for installing custom applications or scripts on shared hosting:
- Check your hosting provider’s terms of service: Before you install any custom applications or scripts, be sure to check your hosting provider’s terms of service to see if there are any restrictions. Some providers may not allow you to install certain types of software, or they may require you to obtain their permission before installing certain applications.
- Only install software from trusted sources: When you install custom applications or scripts, be sure to only install software from trusted sources. This will help to protect your website from malware and other security threats.
- Be aware of your server’s limitations: Shared hosting servers have limited resources, so you need to be aware of your server’s limitations before installing any custom applications or scripts. Installing too many applications or scripts could overload your server and cause performance problems.
- Consult with your hosting provider: If you have any questions about installing custom applications or scripts, be sure to consult with your hosting provider. They may be able to provide you with more specific information about the restrictions on your server.
In general, it is best to avoid installing custom applications or scripts on shared hosting unless you are absolutely sure that they are compatible with your server and that they will not cause any problems. If you need to install custom software, you may want to consider upgrading to a VPS or dedicated hosting plan, which will give you more control over your server environment.
What happens if my website outgrows Shared Hosting resources?
If your website experiences significant growth, you may need to upgrade to a more robust hosting solution like Virtual Private Server (VPS) or Dedicated Hosting to ensure optimal performance.
If your website outgrows the resources provided by a Shared Hosting plan, you may begin to experience performance issues, slow loading times, and other limitations. Shared Hosting is designed for smaller websites with moderate traffic and resource needs. When a website’s demands exceed the capacity of a Shared Hosting environment, several options are available:
- Upgrade to a VPS (Virtual Private Server):
VPS hosting provides more dedicated resources than Shared Hosting. With a VPS, you have a virtualized server environment with a dedicated portion of CPU, RAM, and storage. This allows for greater scalability and better performance compared to Shared Hosting.
- Consider Dedicated Hosting:
Dedicated Hosting involves renting an entire physical server exclusively for your website. This provides the highest level of control, dedicated resources, and performance. It’s suitable for large websites with high traffic and resource-intensive applications.
- Explore Cloud Hosting:
Cloud Hosting is a scalable solution that allows you to utilize resources from a network of virtual servers. It provides flexibility in scaling resources up or down based on demand. This is a good option for websites with varying traffic levels.
- Optimize and Cache Content:
Before upgrading to a higher-tier hosting plan, you can optimize your website by implementing caching mechanisms, compressing images, and minimizing the use of external scripts. This may improve performance without the need for immediate infrastructure changes.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN):
Implementing a Content Delivery Network (CDN) can help distribute your website’s content across multiple servers globally. This reduces latency and improves page loading times, especially for users in different geographic locations.
- Database Optimization:
Optimize your website’s database by cleaning up unnecessary data, optimizing queries, and implementing indexing. Database performance can significantly impact overall website performance.
- Evaluate Resource Usage:
Monitor your website’s resource usage through the hosting control panel. Identify which resources are reaching their limits, and consider optimizing or upgrading accordingly.
- Consult with Hosting Provider Support:
Contact your hosting provider’s support team to discuss your website’s growth and resource requirements. They can provide insights into available upgrade options and assist with the migration process.
Are there any bandwidth limitations with Shared Hosting?
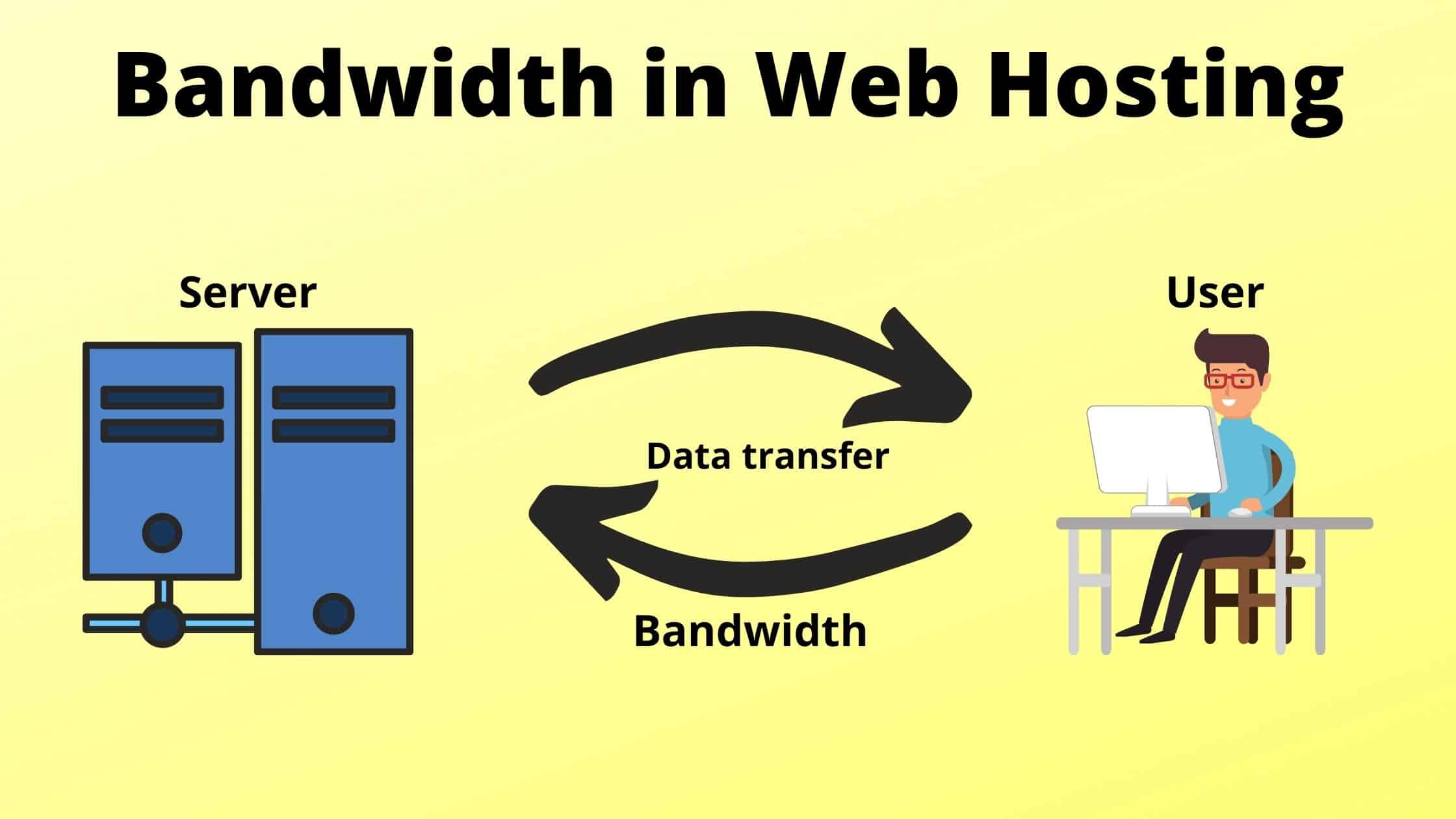
Yes, shared hosting typically has bandwidth limitations. This is because shared hosting servers are designed to handle multiple websites, so they have a limited amount of bandwidth to share among all of the users. Shared hosting plans typically offer a certain amount of bandwidth per month. If you exceed your bandwidth limit, your website may experience slow loading times or downtime.
The specific bandwidth limitations of a shared hosting plan will vary depending on the provider and the plan. Some providers may offer unlimited bandwidth, but this often means that your website’s speed will be throttled if you exceed a certain usage threshold.
If you have a website that is likely to experience high traffic, you may want to consider upgrading to a VPS or dedicated hosting plan. These plans offer more bandwidth and resources, which can help to ensure that your website is always performing at its best.
Key points regarding bandwidth limitations with Shared Hosting:
- Monthly Bandwidth Limits:
Shared Hosting plans often specify a monthly bandwidth limit, which represents the total amount of data that can be transferred to and from your website within a given month. This includes all website content, files, images, and any data exchanged with visitors.
- Overage Charges:
Some hosting providers may charge additional fees if you exceed the allocated monthly bandwidth. It’s essential to be aware of any overage charges and understand the pricing structure in case your website’s traffic surpasses the specified limits.
- Traffic Peaks:
Shared Hosting is suitable for websites with moderate to low traffic. If your website experiences sudden traffic spikes or consistently high levels of traffic, you may need to consider a hosting solution with higher bandwidth allocations, such as VPS or Dedicated Hosting.
- Monitoring and Notifications:
Hosting providers typically offer tools for monitoring bandwidth usage through the hosting control panel. Regularly check these metrics to stay informed about your website’s resource consumption. Some providers may also send notifications when you approach or exceed your bandwidth limit.
- Considerations for Media-Heavy Websites:
Websites that host large media files, videos, or high-resolution images may consume more bandwidth. If your website is media-heavy, you should carefully assess your bandwidth requirements and consider a hosting plan that accommodates your content needs.
- Scalability Options:
If your website is growing rapidly or has high bandwidth requirements, it’s worth considering hosting solutions that offer greater scalability, such as Cloud Hosting or Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting. These options provide more control over resources and can handle increased traffic more effectively.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN):
Implementing a Content Delivery Network (CDN) can help reduce the strain on your hosting server by distributing static content across multiple servers. This not only improves website performance but can also help manage bandwidth usage more efficiently.
Can I get a dedicated IP address with Shared Hosting?
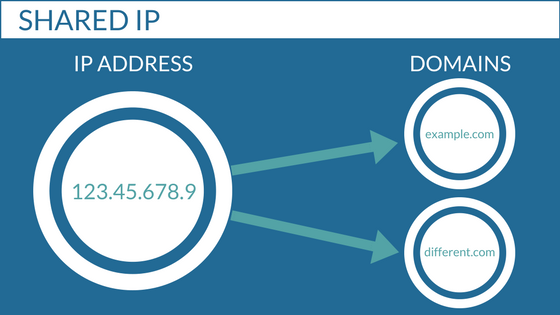
Yes, you can get a dedicated IP address with shared hosting. However, not all shared hosting plans include a dedicated IP address. Some providers offer dedicated IP addresses as an add-on service, while others may only offer them with higher-tier plans.
In many cases, Shared Hosting plans come with a shared IP address, meaning multiple websites on the same server share the same IP address. This is a common practice and is generally sufficient for the majority of websites. However, some hosting providers may offer the option to purchase a dedicated IP address as an add-on or as part of a higher-tier hosting plan.
Some considerations regarding dedicated IP addresses and Shared Hosting:
Shared IP Address:
Shared IP addresses are more common in Shared Hosting environments. Multiple websites share the same IP address, and the server uses techniques like name-based virtual hosting to route requests to the correct website based on the domain name.
Dedicated IP Address:
A dedicated IP address is exclusively assigned to a single hosting account. This means that only your website uses that specific IP address. Dedicated IP addresses can be beneficial for certain scenarios, such as:
- SSL/TLS Certificates: If you need to install a private SSL/TLS certificate for your website (common for e-commerce sites), a dedicated IP address is often required. However, with the widespread adoption of Server Name Indication (SNI), dedicated IPs are less necessary for SSL certificates.
- Email Deliverability: Some users believe that having a dedicated IP address can improve email deliverability, but this is a nuanced topic, and other factors play a role in email delivery.
- Server Access: If you need direct access to your website via IP address for testing or development purposes, a dedicated IP address might be useful.
Cost and Availability:
Dedicated IP addresses may come with an additional cost, either as part of a premium hosting plan or as a separate add-on. Check with your hosting provider to understand the pricing and availability of dedicated IP addresses.
Server Location:
In some cases, users may request a dedicated IP address if they want their website to have a specific geographical location. However, this is not always guaranteed, as it depends on the hosting provider’s infrastructure.
IPv4 vs. IPv6:
With the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses, hosting providers are increasingly adopting IPv6. If you specifically need an IPv4 address, inquire about its availability with your hosting provider.
How often are backups performed on Shared Hosting servers?
The frequency of backups on shared hosting servers varies depending on the hosting provider and the specific plan you choose. However, most shared hosting providers perform backups at least once a week, and some may even perform backups daily or multiple times per day.
The frequency of backups on Shared Hosting servers can vary among hosting providers, and it’s an essential aspect to consider when choosing a hosting plan. Backups are crucial for data recovery in case of accidental data loss, server issues, or other unforeseen events. Here are some considerations regarding backup frequency on Shared Hosting servers:
Daily Backups:
Many hosting providers perform daily backups of Shared Hosting servers. Daily backups are a common practice as they strike a balance between data protection and server resource utilization.
Weekly Backups:
Some hosting providers may opt for weekly backup schedules. While less frequent than daily backups, weekly backups still provide a level of data protection. However, in the event of data loss, there is a potential for a larger amount of data to be unrecoverable compared to daily backups.
Custom Backup Schedules:
Certain hosting providers allow users to configure custom backup schedules based on their preferences. This flexibility can be advantageous for websites with specific requirements or businesses with unique backup policies.
Retention Period:
The retention period refers to how long backups are kept before being replaced by newer backups. Hosting providers typically retain backups for a specific duration, such as one week, one month, or longer. Ensure you are aware of the retention period offered by your hosting provider.
User-Initiated Backups:
Some hosting control panels provide users with the option to initiate backups manually. This allows website owners to create backups at their convenience, especially before making significant changes or updates to their websites.
Offsite Backups:
Offsite backups are copies of data stored in a location separate from the primary server. Some hosting providers offer offsite backup solutions for added security. Offsite backups can be valuable in scenarios where the primary server experiences a catastrophic failure.
Backup Accessibility:
Check whether your hosting provider allows users to access and restore backups independently through the hosting control panel. Having the ability to restore specific files or databases from backups can be essential in case of accidental data loss.
Are SSL certificates included in Shared Hosting plans?

Yes, many shared hosting plans include SSL certificates. Shared hosting providers frequently offer free SSL certificates as part of their plans, making it simple to secure your website and protect user data. You can typically install and configure the SSL certificate quickly and easily through your hosting provider’s control panel.
However, the inclusion of SSL certificates in shared hosting plans varies depending on the provider. Some providers may offer SSL certificates as an add-on service, while others may only offer them with higher-tier plans. Additionally, the type of SSL certificate offered may vary, with some providers offering basic domain validation SSL certificates and others offering more advanced organization or extended validation SSL certificates.
If you’re not sure whether your shared hosting plan includes an SSL certificate, you can check with your hosting provider. They can provide you with details about the type of SSL certificate included and how to install and configure it.
Can I host an e-commerce website on Shared Hosting?
Yes, you can absolutely host an e-commerce website on shared hosting. Shared hosting is a cost-effective and scalable option for small e-commerce businesses and startups. It offers a variety of features that can help you get your e-commerce website up and running quickly and easily.
What level of technical support is provided for Shared Hosting users?

The level of technical support provided for shared hosting users varies depending on the hosting provider. Some providers offer 24/7 support via phone, email, and live chat, while others offer more limited support hours or only via email or ticket systems. Additionally, the quality of technical support can also vary depending on the provider. Some providers have a reputation for providing excellent support, while others may have more limited technical expertise or may be slow to respond to requests.
Factors to consider when evaluating the level of technical support provided for shared hosting users:
- Availability: How quickly can you get help if you have a problem? Do they offer 24/7 support?
- Knowledge base: Do they have a comprehensive knowledge base that can answer common questions?
- Response time: How quickly do they respond to requests for help?
- Expertise: Do they have the expertise to solve complex technical problems?
- Friendliness: Are they friendly and helpful?
You can usually find information about the level of technical support offered by a hosting provider on their website or by contacting their customer support team. It is also a good idea to read reviews of the provider to see what other customers have to say about their technical support.
How does server maintenance and downtime affect Shared Hosting?
Server maintenance and downtime can have a few significant impacts on shared hosting. These impacts can range from minor inconveniences to major disruptions, depending on the frequency and duration of the maintenance or downtime.
How server maintenance and downtime may affect Shared Hosting users:
- Scheduled Maintenance:
Hosting providers regularly perform scheduled maintenance on their servers to ensure optimal performance, security, and the application of updates. During scheduled maintenance, servers may be temporarily taken offline, resulting in downtime for websites hosted on those servers.
- Communication of Maintenance:
Reputable hosting providers communicate scheduled maintenance to users in advance. Users are typically notified through email, the hosting control panel, or other communication channels about the timing and duration of maintenance. This allows website owners to plan accordingly.
- Impact on Website Availability:
During scheduled maintenance, websites hosted on the affected server may be temporarily unavailable. The duration of downtime varies depending on the nature of the maintenance and the efficiency of the hosting provider’s procedures.
- Mitigating Downtime Impact:
Hosting providers often aim to minimize downtime during maintenance by scheduling it during low-traffic periods. Additionally, some providers use redundancy and failover mechanisms to route traffic to alternative servers while maintenance is performed on one server, reducing the impact on users.
- Unscheduled Downtime:
In addition to scheduled maintenance, there can be instances of unscheduled downtime due to unforeseen issues such as hardware failures, network problems, or security incidents. Reputable hosting providers work to minimize such occurrences and promptly address any issues that arise.
- Website Performance During Maintenance:
While maintenance is ongoing, users may experience degraded performance on their websites or temporary unavailability of certain features. This is especially true if maintenance involves critical server components.
- Mitigation Strategies:
Shared Hosting users can take steps to mitigate the impact of downtime during maintenance. This includes informing visitors about scheduled maintenance, scheduling critical activities during non-maintenance periods, and implementing content delivery networks (CDNs) to distribute website content across multiple servers.
- Backup and Restore:
Before scheduled maintenance, it’s advisable for users to perform backups of their websites. In the event of any issues or data loss during maintenance, having a recent backup ensures that websites can be restored to a previous state.
- Hosting Provider Communication:
Hosting providers should maintain open communication with users, keeping them informed about any scheduled maintenance, downtime incidents, and resolutions. Clear and transparent communication helps users understand the status of their hosting services.
Can I use a content management system (CMS) like WordPress with Shared Hosting?

Yes, you can certainly use a content management system (CMS) like WordPress with shared hosting. Shared hosting is a popular type of web hosting that is frequently used for WordPress websites. It is an affordable and scalable option that can accommodate a range of website sizes and traffic levels.
Shared hosting plans typically include pre-installed WordPress software, making it simple to set up your website. Additionally, many shared hosting providers offer one-click WordPress installation tools that can further streamline the process.
Steps to use WordPress with Shared Hosting:
- Select a Shared Hosting Plan:
Choose a Shared Hosting plan from a reputable hosting provider. Many hosting providers offer specific plans optimized for hosting WordPress websites.
- Domain Registration:
If you don’t already have a domain, you may need to register one. Many hosting providers include a free domain registration with their hosting plans.
- Install WordPress:

Most Shared Hosting providers offer easy one-click installations for popular CMS platforms, including WordPress. You can typically install WordPress directly from your hosting control panel. If your hosting provider uses cPanel, Plesk, or a similar control panel, look for an option like “Softaculous” or “Installatron” to install WordPress.
- Configure WordPress:
After installation, you’ll need to configure your WordPress website. This includes setting up your site’s title, tagline, and administrator account. You can also choose a theme and customize your website’s appearance.
- Content Creation:
With WordPress installed, you can start creating and publishing content. WordPress provides an intuitive interface for adding pages, blog posts, images, and other elements to your website.
- Customization with Themes and Plugins:
Explore and install themes to change the look and feel of your website. Additionally, you can enhance the functionality of your site by installing plugins. WordPress has a vast repository of free and premium themes and plugins for various purposes.
- Regular Updates:
Keep your WordPress installation, themes, and plugins up to date to ensure security and take advantage of new features. Many hosting providers offer automatic updates, but it’s good practice to check regularly.
- Security Measures:
Implement security best practices, such as using strong passwords, limiting login attempts, and installing a security plugin. Regularly backup your WordPress site to protect against data loss.
- Performance Optimization:
Optimize your WordPress site for performance by using caching plugins, compressing images, and minimizing unnecessary scripts. This helps ensure that your website loads quickly and efficiently.
Are there any restrictions on the types of websites allowed on Shared Hosting?
Yes, there are some restrictions on the types of websites allowed on shared hosting. These restrictions are in place to protect the integrity of the shared hosting servers and to ensure that all websites have a fair chance of performing well.
General restrictions on the types of websites allowed on shared hosting:
- Websites that use excessive resources: Shared hosting servers have limited resources, so websites that use a lot of CPU power, RAM, or disk space are not allowed. This includes websites with high traffic levels, websites that use streaming video or audio, and websites that store large files.
- Websites that are illegal or harmful: Shared hosting providers are not allowed to host websites that contain illegal content, such as pornography, gambling, or copyrighted material. They also are not allowed to host websites that are designed to harm others, such as malware or phishing websites.
- Websites that are abusive or disruptive: Shared hosting providers reserve the right to terminate the accounts of websites that are abusive or disruptive. This includes websites that send spam email, websites that participate in denial-of-service attacks, and websites that contain excessive advertising.
Is there an option for domain registration with Shared Hosting plans?
Yes, many shared hosting plans include domain registration as an add-on service or as part of the plan. This means that you can purchase a new domain name when you sign up for a shared hosting plan, or you can transfer an existing domain name to your new hosting provider.
The cost of domain registration typically varies depending on the domain registrar and the extension (.com, .net, etc.). However, most shared hosting providers offer competitive prices for domain registration, and some may even include a free domain name with certain plans.
How does email hosting work with Shared Hosting?

Email hosting is a type of web hosting that allows you to create and manage email addresses for your domain name. Shared hosting is a common type of web hosting that typically includes email hosting as a standard feature.
Yes, many Shared Hosting providers offer domain registration services as part of their hosting packages. When you sign up for a Shared Hosting plan, you may have the option to register a new domain, transfer an existing domain from another registrar, or use an already registered domain.
How domain registration typically works with Shared Hosting:
- New Domain Registration:
When you sign up for a Shared Hosting plan, the hosting provider often offers the option to register a new domain. You can search for available domain names, select a domain extension (e.g., .com, .net, .org), and complete the registration process during the hosting account setup.
- Domain Transfer:
If you already have a domain registered with another registrar and want to consolidate your hosting and domain management, you can transfer the domain to your new hosting provider. The domain transfer process involves updating the domain’s registrar information and may include an additional fee.
- Using an Existing Domain:
If you already own a domain registered with a different registrar, you can use it with your Shared Hosting plan. During the setup process, you would update the domain’s DNS (Domain Name System) settings to point to the name servers provided by your hosting provider.
- Included or Additional Cost:
Some hosting providers include a free domain registration as part of their Shared Hosting plans for the initial term. Others may offer domain registration as an additional service with separate pricing. Be sure to check the specific offerings of your chosen hosting provider.
- Domain Management:
Shared Hosting providers typically offer domain management tools within their hosting control panels. These tools allow you to configure domain settings, manage DNS records, set up email associated with the domain, and perform other domain-related tasks.
- Renewal Fees:
Keep in mind that domain registration is typically billed annually, and there are renewal fees to maintain ownership of the domain. Some hosting providers offer automatic domain renewal, while others may require manual renewal.
What security measures are in place to protect Shared Hosting servers?
Shared hosting providers implement a variety of security measures to protect their servers and the websites hosted on them. These measures are designed to prevent unauthorized access, malware infections, and other security threats.
Security is a critical aspect of Shared Hosting, and hosting providers implement various measures to protect their servers and the websites hosted on them. While specific security measures can vary between hosting providers, here are common security features and practices implemented to safeguard Shared Hosting servers:
- Firewall Protection:
Shared Hosting servers are typically equipped with firewalls that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. Firewalls help prevent unauthorized access, protect against malicious activities, and filter potentially harmful traffic.
- DDoS Protection:
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks can overwhelm a server by flooding it with traffic. Shared Hosting providers often implement DDoS protection mechanisms to detect and mitigate such attacks, ensuring server stability and availability.
- Server Monitoring:
Continuous monitoring of server activity allows hosting providers to identify and address any abnormal behavior or security incidents promptly. Monitoring tools help detect unauthorized access, resource abuse, or other suspicious activities.
- Regular Software Updates:
Hosting providers regularly update server software, including the operating system, web server (e.g., Apache, Nginx), and other components. Keeping software up to date helps patch security vulnerabilities and ensures a secure hosting environment.
- Security Patches:
In addition to routine updates, providers promptly apply security patches to address newly discovered vulnerabilities. This helps protect against potential exploits and enhances the overall security posture of the server.
- Malware Scanning and Removal:
Shared Hosting servers are often equipped with malware scanning tools that continuously monitor for malicious files or scripts. If malware is detected, hosting providers take action to quarantine or remove the infected files.
Can I customize server configurations in Shared Hosting?
In a traditional Shared Hosting environment, the level of customization for server configurations is often limited compared to other hosting solutions like Virtual Private Servers (VPS) or Dedicated Servers. Shared Hosting is designed to be a simplified and user-friendly hosting solution, and as such, many server configurations are managed by the hosting provider to maintain stability and security across shared environments.
Shared hosting typically offers limited customization options for server configurations. This is because shared hosting servers are designed to accommodate multiple websites, so the hosting provider needs to maintain a consistent configuration for all users. However, there are some basic server configurations that you may be able to customize, such as:
- Control Panel Settings:
Shared Hosting providers typically offer a control panel (e.g., cPanel, Plesk) that allows users to manage various aspects of their hosting accounts. While these control panels provide a degree of customization for website and email settings, they may not offer advanced server-level configurations.
- Limited Server Access:
Shared Hosting accounts are isolated from each other for security reasons. Users have access to their individual hosting accounts, but they do not have direct access to server-level configurations or settings. This limitation is in place to prevent users from affecting the overall server environment.
- Server Modules and Software:
The selection of server modules, software versions, and configurations is typically managed by the hosting provider. Users may not have the ability to install or configure server-level software beyond what is provided by the hosting environment.
- Custom PHP Configuration:
Some Shared Hosting plans may allow users to customize certain PHP settings for their websites, such as memory limits, file upload sizes, and error reporting. However, the extent of customization may be restricted to prevent users from negatively impacting server performance.
What is the process for migrating a website to a Shared Hosting plan?
Migrating a website to a shared hosting plan involves several steps, including backing up your website files and database, exporting your website’s content, and importing it into the new hosting environment.
Overview of the process step by step:
Step 1: Back up your website files and database
Before making any changes to your website, it’s crucial to create a complete backup of your website files and database. This ensures that you have a copy of your website in case something goes wrong during the migration process.
Step 2: Export your website’s content
The next step is to export your website’s content from your current hosting provider. This may involve using a migration plugin or manually downloading your website files and database.
Step 3: Create a new database and import your website’s content
Once you have exported your website’s content, you need to create a new database and import your website’s content into it. This can usually be done through your new hosting provider’s control panel.
Step 4: Update your website’s configuration settings
After importing your website’s content, you may need to update your website’s configuration settings to reflect the new hosting environment. This may include changing the database connection details, updating file paths, and configuring any plugins or themes.
Step 5: Test your website
Once you have completed the migration process, it’s essential to test your website thoroughly to ensure that everything is working properly. Check for broken links, missing images, and any other functionality issues.
How does server location impact website performance in Shared Hosting?
The location of the server where your website is hosted can significantly impact your website’s performance. This is because the data for your website needs to travel from the server to the visitor’s browser, and the further the server is from the visitor, the longer this journey will take. This can lead to slow loading times, delayed responses, and a poor user experience.
Some specific ways in which server location can impact website performance:
- Latency: Latency is the time it takes for data packets to travel between the server and the visitor’s browser. The higher the latency, the longer it will take for your website’s pages to load.
- Packet loss: Packet loss occurs when data packets are lost during transmission. This can cause errors and delays in loading your website’s content.
- Jitter: Jitter is the variation in latency over time. High jitter can make your website appear to be slow and unresponsive.
Are there any resource usage policies in Shared Hosting?
Yes, Shared Hosting providers typically implement resource usage policies to ensure fair and equitable distribution of server resources among multiple users sharing the same server. These policies are in place to maintain server stability, prevent resource abuse, and provide a reliable hosting environment for all users. Common resource usage policies in Shared Hosting include:
Common resource usage policies in shared hosting include:
- CPU usage limits: Shared hosting plans typically have limits on the amount of CPU power that a single website can use. This prevents websites from using too much CPU power and slowing down other websites on the server.
- RAM usage limits: Shared hosting plans also have limits on the amount of RAM that a single website can use. This prevents websites from using too much RAM and causing memory leaks that can crash the server.
- IO usage limits: Shared hosting plans may also have limits on the amount of input/output (IO) that a single website can use. This prevents websites from using too much IO and causing performance bottlenecks for other websites on the server.
- Entry process limits: Shared hosting plans may also have limits on the number of concurrent entry processes that a single website can use. This prevents websites from using too many threads or processes and causing performance problems for other websites on the server.
- File size limits: Shared hosting plans often have limits on the size of individual files that can be uploaded to the server. This prevents users from uploading large files that could take up too much disk space or slow down the server.
- Account suspension: Shared hosting providers may suspend accounts that exceed their resource usage limits or violate the provider’s terms of service. This is done to protect the integrity of the server and ensure that all websites have a fair chance of performing well.
Can I upgrade or downgrade my Shared Hosting plan as needed?
Yes, you can usually upgrade or downgrade your shared hosting plan as needed. This is a great way to adjust your hosting resources to match your changing needs.
Upgrading your Shared Hosting plan
If your website is experiencing high traffic or you require more resources, you can upgrade to a higher-tier shared hosting plan. This will give you access to more CPU power, RAM, and disk space, which can improve your website’s performance and accommodate more visitors.
Downgrading your Shared Hosting plan
If your website is experiencing low traffic and you don’t need as many resources, you can downgrade to a lower-tier shared hosting plan. This can save you money on your monthly hosting costs.
Considerations when upgrading or downgrading your plan
When upgrading or downgrading your shared hosting plan, there are a few things to keep in mind:
- Data migration: If you are upgrading your plan, you will need to migrate your website data to the new server. This can be done by your hosting provider or by yourself using a migration plugin or tool.
- Downtime: Upgrading or downgrading your plan may result in some downtime for your website. Your hosting provider should notify you of any planned downtime in advance.
- Plan limitations: Be sure to check the limitations of the new plan before upgrading or downgrading. This will ensure that the plan meets your needs and that you are not overpaying for resources you don’t use.
Contact your hosting provider
If you have any questions about upgrading or downgrading your shared hosting plan, contact your hosting provider. They will be able to help you determine the best plan for your needs and guide you through the process of changing your plan.
What is the average response time for customer support inquiries in Shared Hosting?
The average response time for customer support inquiries in Shared Hosting can vary widely depending on the hosting provider’s policies, support infrastructure, and the nature of the support request. Different hosting companies may have different service level agreements (SLAs) outlining their commitment to responding to customer inquiries within a certain timeframe.
Tier of Support:
Hosting providers often offer multiple support tiers, such as basic, standard, and premium support. The response time can vary based on the level of support you have chosen. Premium or priority support plans typically come with faster response times.
Type of Inquiry:
The urgency and complexity of the support request can influence response times. Critical issues that impact the availability of your website may receive faster attention than general inquiries or requests for information.
Communication Channels:
Hosting providers typically offer various communication channels, including ticket systems, live chat, and phone support. Response times may vary depending on the channel you use. Live chat and phone support tend to offer quicker responses than ticket systems.
Time of Day and Day of Week:
The time of day and the day of the week can also impact response times. During peak hours or weekends, support teams may experience higher volumes of inquiries, potentially leading to slightly longer response times.
Provider Policies and SLAs:
Review the hosting provider’s support policies and SLAs to understand their commitments regarding response times. This information is often available on their website or in the terms of service.
Are there any restrictions on the number of databases in Shared Hosting plans?
Yes, there are typically restrictions on the number of databases that you can create on a Shared Hosting plan. This is because shared hosting servers are designed to accommodate multiple websites, so the hosting provider needs to limit the number of databases that each website can use in order to ensure that all websites have access to the resources they need.
The exact number of databases that you are allowed to create will vary depending on the hosting provider and the specific plan that you choose. However, most shared hosting plans will allow you to create at least 10 databases. If you need more than this, you may need to upgrade to a VPS or dedicated hosting plan.
Database Limitations:
Shared Hosting plans often have a predefined limit on the number of databases a user can create. This limit is set to ensure fair resource allocation among multiple users sharing the same server.
Database Types:
Shared Hosting plans commonly support popular database management systems like MySQL or PostgreSQL. The number of databases allowed may vary based on the hosting provider and the specific database management system offered.
Additional Features:
Some higher-tier Shared Hosting plans may offer more databases as well as additional features, such as support for larger databases, increased storage, or improved performance. Be sure to review the features of each plan to determine the one that best suits your needs.
Database Size Limits:
In addition to the number of databases, hosting providers may impose limits on the size of individual databases. This limitation helps prevent one user from monopolizing too much storage space on the shared server.
Considerations for Web Applications:
If your website relies on content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, Joomla, or Drupal, each installation typically requires a database. Consider the number of installations and associated databases needed for your web applications.
Database Management Tools:
Shared Hosting plans often come with database management tools accessible through the hosting control panel. These tools allow users to create, manage, and interact with their databases efficiently.
Upgrading for Additional Databases:
If your website grows, and you find that you need more databases than your current plan allows, consider upgrading to a higher-tier Shared Hosting plan or exploring other hosting options, such as Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting, which offers more flexibility in terms of resource allocation.
Check Hosting Provider’s Policies:
Review the terms of service and acceptable use policy of your hosting provider to understand the specific limitations on databases. This information is usually outlined in the documentation provided by the hosting company.
Can I use my own SSL certificate with Shared Hosting?
Whether or not you can use your own SSL certificate with Shared Hosting depends on the hosting provider. Some hosting providers allow you to import your own SSL certificate, while others only allow you to use SSL certificates that they provide.
Some factors that determine whether or not you can use your own SSL certificate with Shared Hosting:
The type of hosting plan: Some shared hosting plans include free SSL certificates, while others do not. If your plan does not include a free SSL certificate, you may be able to purchase one from your hosting provider or from a third-party SSL certificate provider.
The hosting provider’s policies: Some hosting providers have policies that restrict the use of custom SSL certificates. For example, they may only allow you to use SSL certificates that are issued by certain certificate authorities (CAs).
The server configuration: In some cases, the server configuration may prevent you from installing your own SSL certificate. This is more likely to be the case with very low-cost shared hosting plans.
What backup options are available for Shared Hosting users?
Backup options for Shared Hosting users can vary depending on the hosting provider and the specific plan you are subscribed to. Here are common backup options and features that may be available:
Provider-Generated Backups:
Many Shared Hosting providers offer automated backup solutions as part of their service. These backups are typically generated by the hosting provider at regular intervals (daily, weekly, or monthly) and are stored on a separate server or storage system.
Backup Frequency:
Check with your hosting provider to understand how frequently they perform backups. Some providers offer daily backups, while others may have less frequent intervals. The more frequent the backups, the more up-to-date your backup will be in the event of data loss.
Backup Retention Period:
Providers often retain backup copies for a specific period. For example, they may keep daily backups for the past seven days, weekly backups for the past four weeks, and monthly backups for the past three months. Ensure you understand the retention policy of your hosting provider.
Backup Accessibility:
Verify how easily you can access and restore data from the backups. Some hosting providers offer a user-friendly interface within the hosting control panel that allows you to restore specific files or the entire website from a backup.
Manual Backups:
Some hosting providers allow users to create manual backups on-demand. This feature can be useful before making significant changes to your website, such as updating plugins or themes, ensuring you have a backup to revert to if needed.
Backup Download Options:
Check if your hosting provider allows you to download backup files. This can be valuable if you want to store backups locally or if you plan to migrate your website to a different hosting provider.
Remote Backup Storage:
In addition to on-server backups, some hosting providers offer remote backup storage options. This involves storing backup copies in a separate location or on a cloud-based storage service for added redundancy.
Backup Restoration Assistance:
Understand the process of restoring your website from a backup. Some hosting providers offer support or documentation to guide users through the restoration process, while others may provide assistance through their support team.
Backup Plugins or Tools:
Depending on the hosting platform (such as WordPress), there may be backup plugins or tools available that enable you to create and manage backups independently of the hosting provider’s system.
Custom Backup Solutions:
For users with specific backup requirements, some hosting providers may offer custom backup solutions or additional features. This could include options for more frequent backups, longer retention periods, or specialized backup configurations.
How does Shared Hosting handle traffic spikes?
Shared Hosting plans have certain limitations when it comes to handling traffic spikes, and the ability to manage increased website traffic depends on various factors.
How Shared Hosting typically handles traffic spikes:
Shared Resources:
In Shared Hosting, multiple websites share resources on the same server. When one website experiences a traffic spike, it can potentially affect the performance of other websites on the same server. The shared nature of resources means that each website has a portion of the server’s resources allocated to it.
Server Overload:
If a website on the shared server receives a sudden surge in traffic, it may use a larger portion of the available resources (CPU, memory, bandwidth). This can potentially lead to slower response times for other websites on the server, especially during the duration of the traffic spike.
Resource Limits:
Shared Hosting plans often come with resource limits, such as maximum CPU usage, memory allocation, and bandwidth. If a website exceeds these limits, the hosting provider may take measures to prevent one site from monopolizing resources and negatively impacting others. This can include throttling or temporarily suspending the resource-intensive website.
Temporary Performance Impact:
During a traffic spike, the server may experience a temporary increase in load. This can result in slower response times for all websites on the server until the spike subsides. Shared Hosting is generally well-suited for websites with moderate and consistent traffic rather than those with frequent and significant spikes.
Caching Strategies:
Some Shared Hosting providers implement caching strategies to help mitigate the impact of traffic spikes. Caching involves storing static copies of web pages so that they can be served quickly without generating dynamic content for each request. Caching can significantly improve website performance during traffic spikes.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs):
Utilizing a Content Delivery Network (CDN) can distribute the load and help mitigate the impact of traffic spikes. CDNs cache static content on servers located in various geographic regions, reducing the load on the main hosting server and improving the delivery of content to users.
Communication with Hosting Support:
If you anticipate significant traffic spikes or experience sudden increases in traffic, it’s advisable to communicate with your hosting provider’s support team. They can offer guidance and may be able to implement temporary solutions or optimizations to help manage the increased load.
Consideration for Resource-Intensive Applications:
Resource-intensive applications, such as complex databases or dynamic scripts, can contribute to increased server load during traffic spikes. Shared Hosting may have limitations for hosting such applications, and users with resource-intensive needs may consider alternatives like Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting.
Can I set up subdomains with Shared Hosting?
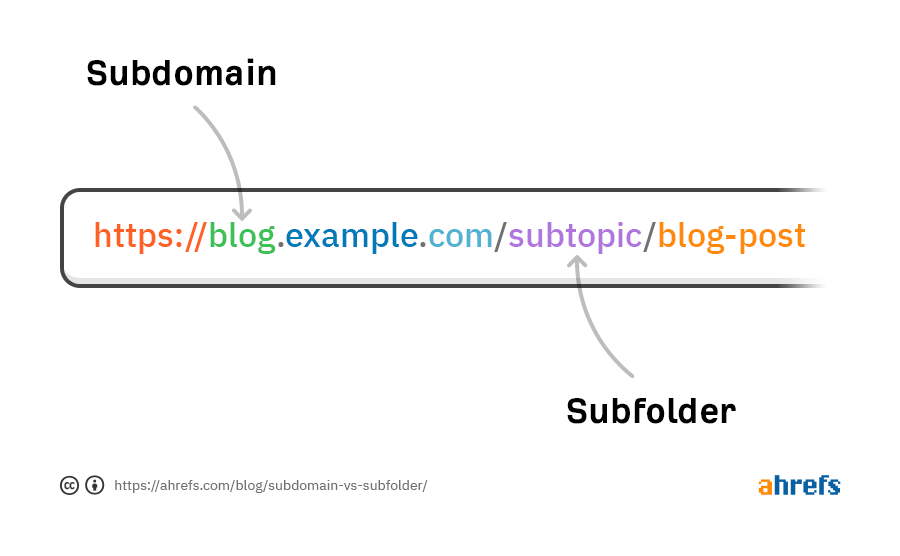
Yes, in most cases, you can set up subdomains with Shared Hosting. A subdomain is a subdirectory of a domain name that is used to create a separate website or section of a website. For example, you could create a subdomain called “blog” for your website to create a separate blog section.
To set up a subdomain with Shared Hosting, you will need to access your hosting provider’s control panel. Once you are logged in, you will need to find the section that deals with domains and subdomains. From there, you will be able to create a new subdomain by entering the desired subdomain name and selecting the domain name that you want to use.
Once you have created the subdomain, you will need to create a directory for it on your server. You can do this using an FTP client or by accessing your hosting provider’s file manager. Once you have created the directory, you will need to upload your website files to it.
After you have uploaded your website files, you will need to point the subdomain to the directory that you created. You can do this by editing the DNS records for the subdomain. The specific steps for editing DNS records will vary depending on your hosting provider, but you should be able to find instructions in their documentation.
Once you have pointed the subdomain to the correct directory, your subdomain should be up and running. You can test it by visiting the subdomain URL in your web browser.
What is the policy on account suspension or termination in Shared Hosting?
The specific policy on account suspension or termination in Shared Hosting varies depending on the hosting provider. However, there are some general guidelines that most providers follow.
Account Suspension
An account is typically suspended if it violates the hosting provider’s terms of service. This may include:
- Non-payment of hosting fees
- Exceeding resource usage limits
- Engaging in illegal activity, such as spamming or copyright infringement
- Uploading malicious files, such as viruses or malware
If your account is suspended, you will receive a notification from your hosting provider. You will be given the opportunity to correct the violation and have your account reinstated. However, if you fail to correct the violation, your account may be terminated.
Account Termination
An account is typically terminated if it cannot be reinstated after suspension or if it poses a serious threat to the hosting provider’s network. This may include:
- Repeated violations of the terms of service
- Engaging in activity that could cause harm to other users or to the hosting provider’s infrastructure
- Being the target of a sustained cyberattack
If your account is terminated, you will lose access to your website and your data. You will also be responsible for any outstanding hosting fees.
Preventing Account Suspension or Termination
To prevent your account from being suspended or terminated, it is important to:
- Read and understand your hosting provider’s terms of service
- Pay your hosting fees on time
- Use your account responsibly
- Keep your website and software up to date
- Scan your website for malware regularly
- Avoid engaging in illegal activity or uploading malicious files
By following these guidelines, you can help to ensure that your account remains in good standing and that your website is protected from suspension or termination.
How does Shared Hosting impact website loading speed?
While Shared Hosting is generally suitable for small to medium-sized websites, it’s important to optimize your website for performance. Implementing speed optimization techniques can enhance loading times. Shared hosting can impact website loading speed in several ways, both positively and negatively.
Positive Impacts
- Sharing resources: Shared hosting servers distribute resources among multiple websites, which can help to reduce the load on any single server and improve overall performance.
- Caching: Shared hosting providers often implement caching mechanisms to store frequently accessed content, such as images and CSS files, in memory. This can reduce the need to retrieve these files from the server, which can improve page load times.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Many shared hosting providers offer or integrate with CDNs, which distribute static content across multiple servers worldwide. This can significantly reduce latency and improve page load times for visitors located far from the origin server.
Negative Impacts
- Resource contention: When multiple websites share a single server, they also share the server’s resources, such as CPU, RAM, and disk space. If one website experiences a sudden surge in traffic, it can consume a disproportionate amount of resources, which can slow down other websites on the server.
- Software limitations: Shared hosting providers often have limitations on the software that can be installed on their servers. This can limit your ability to optimize your website for performance.
- Inadequate hardware: Shared hosting servers may not have the latest hardware, which can limit their ability to handle high traffic volumes or resource-intensive websites.
Optimizing Website Loading Speed on Shared Hosting
Despite the potential drawbacks, there are several things you can do to optimize website loading speed on shared hosting:
- Choose a reputable hosting provider: A reliable hosting provider with a good reputation for uptime and performance is essential for maintaining a fast-loading website.
- Optimize your website’s code: Use efficient coding practices, minimize file sizes, and optimize images to reduce page load times.
- Enable caching: Utilize caching plugins or server-side caching mechanisms to store frequently accessed content in memory, reducing the need to retrieve it from the database or file system.
- Use a CDN: Integrate a CDN to distribute static content across multiple servers worldwide, reducing latency and improving page load times for global visitors.
- Monitor website performance: Regularly monitor your website’s performance using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to identify and address potential bottlenecks.
Are there any restrictions on the use of third-party applications or plugins in Shared Hosting?
Yes, there are often restrictions on the use of third-party applications or plugins in Shared Hosting. This is because shared hosting providers need to maintain a consistent and stable environment for all of their customers.
The use of third-party applications or plugins in Shared Hosting is generally allowed, but there are often some considerations and potential restrictions. These restrictions are in place to ensure the security, stability, and fair usage of resources on the shared server. Here are common considerations regarding third-party applications or plugins on Shared Hosting:
Compatibility:
Shared Hosting providers typically support a wide range of popular applications and plugins. However, it’s essential to verify that the third-party applications or plugins you want to use are compatible with the server environment and meet the hosting provider’s requirements.
Security Concerns:
Hosting providers may restrict or disallow certain applications or plugins if they pose security risks. This can include applications with known vulnerabilities or those that may compromise the overall security of the server.
Resource Usage:
Shared Hosting plans come with predefined resource allocations. Some applications or plugins, especially resource-intensive ones, may exceed these limits, leading to performance issues for your website and potentially impacting other users on the same server.
Server Configuration:
Certain applications or plugins may require specific server configurations or settings. Shared Hosting providers often configure servers for general compatibility, and users may have limited control over server settings. Ensure that your chosen applications or plugins do not require configurations that are not supported in a shared environment.
Plugin/Script Restrictions:
Some hosting providers may have restrictions on specific types of plugins or scripts. For example, certain executable scripts or scripts that consume excessive server resources may be restricted.
Terms of Service and Acceptable Use Policy:
The hosting provider’s terms of service (ToS) and acceptable use policy (AUP) outline the rules and guidelines for using their hosting services. Be sure to review these documents to understand any restrictions or guidelines related to third-party applications or plugins.
Support and Updates:
While hosting providers may allow the use of third-party applications or plugins, they may not provide support for these external tools. It’s important to rely on the support channels provided by the application/plugin developers for assistance.
Automatic Updates:
Some hosting providers automatically update server software for security and stability. If a third-party application or plugin requires specific software versions, automatic updates could potentially impact compatibility. Check with your hosting provider for information on their update policies.
Can I host a database-driven website on Shared Hosting?
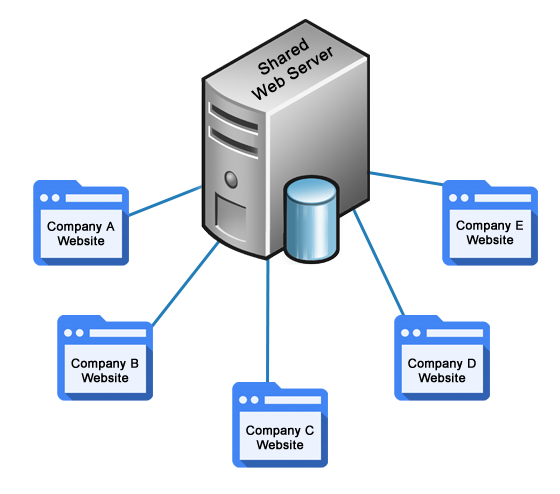
Yes, you can host a database-driven website on Shared Hosting, and it is actually a common way to do so. Shared hosting is a type of web hosting where multiple websites share a single server. This makes it a cost-effective option for many websites, including those that use databases.
Most shared hosting plans include a MySQL database, which is the most popular type of database for websites. You can also use other types of databases, such as PostgreSQL or MariaDB, with some shared hosting providers.
To host a database-driven website on shared hosting, you will need to create a database and then import your website’s content into it. You will also need to configure your website to connect to the database.
How does Shared Hosting handle software updates for server applications?
Shared hosting providers typically have their own procedures for handling software updates for server applications. These procedures are designed to ensure that updates are installed smoothly and without disrupting your website.
How shared hosting providers handle software updates for server applications:
1. Testing and Validation
Before deploying any software updates to the shared hosting environment, the hosting provider will thoroughly test the updates in a staging environment. This involves evaluating the update’s compatibility with the existing server configuration, identifying potential conflicts or issues, and ensuring that the update doesn’t introduce any bugs or performance regressions.
2. Scheduling Updates
Software updates are typically scheduled during off-peak hours to minimize disruption to website users. Hosting providers carefully plan the update schedule, considering factors like server traffic patterns, maintenance windows, and potential impact on user experience.
3. Phased Deployment
For critical updates, hosting providers may employ a phased deployment approach. This involves rolling out the update to a small subset of servers first, monitoring the impact on performance and stability, and gradually expanding the rollout to the rest of the shared hosting environment once the update is deemed stable and secure.
4. Notifications and Rollbacks
Shared hosting providers usually notify customers in advance of upcoming software updates. This allows users to prepare their websites for any potential changes or compatibility issues. Additionally, most hosting providers have rollback procedures in place, enabling them to revert to the previous software version if the update causes unexpected problems.
5. Monitoring and Support
After deploying software updates, hosting providers closely monitor server performance and user feedback to identify any issues that may arise. They also provide support to customers who encounter problems related to the update, assisting them in troubleshooting and resolving any incompatibilities.
Is there a trial period or money-back guarantee with Shared Hosting plans?

Many Shared Hosting providers offer a trial period or a money-back guarantee as part of their service. However, the terms and duration of these guarantees can vary among hosting companies. Here are some common practices related to trial periods and money-back guarantees for Shared Hosting plans:
Money-Back Guarantee:
Some hosting providers offer a money-back guarantee that allows customers to request a refund within a specified period after signing up for a Shared Hosting plan. This period is typically 30 days, but it can range from 7 days to 60 days or more, depending on the provider.
Trial Period:
Some hosting companies may use the term “trial period” to describe the initial period during which customers can try out their services. This may or may not include a refund option. During this period, users can assess the hosting environment, test website performance, and evaluate the features provided.
Refund Conditions:
Money-back guarantees often come with specific conditions. These conditions may include restrictions on the refundable amount, exclusions for certain fees (e.g., domain registration fees), and requirements for canceling the service within the stipulated timeframe.
No-Risk Trials:
Some hosting providers advertise “no-risk trials” that allow users to sign up for a Shared Hosting plan without an initial payment. The user is billed only after the trial period expires. If the user decides to continue, they are charged; otherwise, they can cancel without any payment.
Free Trials and Freemium Models:
A few hosting providers offer free trials or freemium models, providing a limited version of their Shared Hosting services for free. This allows users to explore the platform and its features before deciding to upgrade to a paid plan.
Check Terms of Service:
Before signing up for a Shared Hosting plan, carefully review the hosting provider’s terms of service (ToS) and refund policy. These documents outline the specific conditions and details related to trial periods, money-back guarantees, and refund processes.
Customer Support Assistance:
If you have questions about the trial period or money-back guarantee, don’t hesitate to contact the hosting provider’s customer support. They can provide clarification on the terms and conditions, ensuring that you have a clear understanding of the hosting service’s policies.
What security features are in place to protect against DDoS attacks in Shared Hosting?
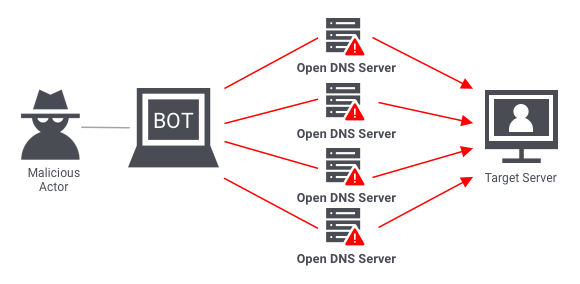
Shared hosting providers employ a combination of security measures to protect against DDoS attacks, ensuring that their customers’ websites remain accessible and protected from malicious traffic.
These measures include:
Network-level DDoS protection: Shared hosting providers often have dedicated network infrastructure specifically designed to mitigate DDoS attacks. This infrastructure can filter out malicious traffic before it reaches the shared servers, protecting all websites hosted on those servers.
Application-level firewalls (WAFs): WAFs act as a barrier between websites and incoming traffic, inspecting and filtering incoming requests to identify and block malicious traffic patterns associated with DDoS attacks. WAFs can be configured to detect and block various types of DDoS attacks, such as SYN floods, HTTP floods, and UDP floods.
Rate limiting: Rate limiting mechanisms restrict the number of requests that can be made from a single source within a specific period, preventing a single attacker from overwhelming a server with excessive traffic. This technique can effectively mitigate DDoS attacks that rely on flooding the server with a large volume of requests.
Blackholing: Blackholing involves redirecting malicious traffic to a null route, effectively removing it from the internet and preventing it from reaching the target server. This technique can be effective in stopping specific types of DDoS attacks, such as DNS amplification attacks.
Geolocation filtering: Geolocation filtering allows shared hosting providers to block traffic from certain regions or countries known to be sources of DDoS attacks. This technique can reduce the impact of DDoS attacks originating from specific geographic locations.
Traffic scrubbing: Traffic scrubbing involves inspecting and analyzing incoming traffic to identify and remove malicious packets or data before it reaches the target server. This technique can help to filter out malicious traffic without affecting legitimate traffic.
Proactive monitoring and alerting: Shared hosting providers continuously monitor network traffic and server performance to detect and respond to DDoS attacks promptly. They often use alert systems to notify their staff or customers of potential DDoS attacks, allowing them to take immediate action.
Customer education and awareness: Shared hosting providers educate their customers about DDoS attacks and provide guidance on how to protect their websites. This includes recommending security plugins, implementing strong passwords, and keeping website software up to date.
How does Shared Hosting impact SEO for my website?

Shared Hosting can impact SEO (Search Engine Optimization) for your website in various ways, but it’s important to note that the impact is indirect. SEO is influenced by a combination of factors, and while the type of hosting you choose is one of them, there are many other aspects to consider.
How Shared Hosting can impact SEO:
1. Website Speed:
Positive Impact: Shared Hosting can affect website speed, and page loading speed is a known SEO ranking factor. If the server resources are well-managed by the hosting provider, your website can load quickly and provide a positive user experience.
Optimization Tip: Implement optimization techniques, such as image compression, browser caching, and content delivery networks (CDNs), to enhance website speed.
2. Server Downtime:
Negative Impact: Shared Hosting servers may experience downtime if there are issues with server maintenance, resource overuse, or technical problems. Downtime can negatively affect SEO by impacting search engine crawlers’ ability to access and index your site.
Optimization Tip: Choose a reliable Shared Hosting provider with a good uptime record and promptly address any technical issues that may arise.
3. Server Location:
Impact: The physical location of the server can influence website speed, especially for visitors in specific geographic regions. Search engines may consider server location as a minor factor in determining local search rankings.
Optimization Tip: Choose a hosting provider with servers located strategically based on your target audience. Some providers offer server locations in different regions.
4. IP Reputation:
Impact: Shared Hosting means that multiple websites share the same IP address. If one of the websites on the same server engages in spam or other malicious activities, it could potentially impact the IP’s reputation.
Optimization Tip: Select a reputable hosting provider that actively monitors and manages server security to prevent abuse.
5. Resource Limitations:
Impact: Shared Hosting plans come with resource limitations. If your website exceeds these limits, it may experience slowdowns or temporary suspension, which can impact SEO.
Optimization Tip: Monitor resource usage, optimize scripts and images, and consider upgrading to a higher hosting plan or a more advanced hosting solution if resource needs increase.
6. Security Measures:
Impact: Shared Hosting providers implement security measures to protect websites on their servers. A secure hosting environment can positively influence SEO by preventing hacks and ensuring data integrity.
Optimization Tip: Use secure passwords, keep software (including CMS and plugins) updated, and follow best security practices for your website.
7. SSL Certificates:
Positive Impact: Search engines consider SSL encryption as a positive ranking factor. Many Shared Hosting providers offer free SSL certificates, enabling you to secure your website and contribute to SEO.
Optimization Tip: Ensure that your hosting plan includes SSL support, and enable SSL for your website.
Can I use my own domain name with Shared Hosting?
Yes, you can use your own domain name with Shared Hosting. Most providers offer domain registration services, or you can use a domain registered with a different provider.
What measures are in place to prevent unauthorized access to Shared Hosting accounts?
Shared Hosting providers implement various security measures to prevent unauthorized access and protect the accounts hosted on their servers. Here are common security measures in place to enhance the protection of Shared Hosting accounts:
Secure Login Credentials:
Shared Hosting providers enforce strong password policies to ensure that users create secure passwords. Users are encouraged to use a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters, and they may be required to update passwords regularly.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
Many hosting providers offer two-factor authentication as an additional layer of security. 2FA requires users to provide a second verification factor (such as a code sent to a mobile device) in addition to the password when logging in.
Secure File Transfer Protocols:
Shared Hosting accounts often support secure file transfer protocols such as SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) or FTPS (FTP Secure). These protocols encrypt data during file transfers, preventing unauthorized interception.
Firewalls:
Hosting providers deploy firewalls at the server level to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. Firewalls help block malicious attempts to access the server and protect against common cyber threats.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS):
Intrusion detection and prevention systems are implemented to monitor network and system activities for signs of malicious behavior. These systems can detect and block unauthorized access attempts.
Server Hardening:
Shared Hosting servers undergo server hardening processes to minimize vulnerabilities and enhance security. This includes disabling unnecessary services, applying security patches promptly, and configuring server settings securely.
Regular Security Audits:
Hosting providers perform regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential security risks. This proactive approach helps ensure that the server environment remains secure.
Isolation between Accounts:
Shared Hosting servers are designed to provide isolation between user accounts. Security measures are in place to prevent one user’s account from accessing the files or data of another user on the same server.
Account Isolation:
Hosting providers use techniques such as chroot (change root) or virtualization to isolate user accounts from each other. This helps contain potential security breaches and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Regular Software Updates:
Hosting providers keep server software, including the operating system, web server, and other components, up to date with the latest security patches. Regular updates help address known vulnerabilities and improve overall server security.
Monitoring and Logging:
Server activities are monitored, and logs are maintained to track user access, changes to files, and other events. Monitoring and logging are essential for detecting and investigating security incidents.
Educational Resources:
Hosting providers often offer educational resources and guidelines to help users understand and implement security best practices. This may include tips on securing websites, managing passwords, and recognizing phishing attempts.
How does Shared Hosting support different programming languages?

Shared hosting supports different programming languages by providing a server environment that includes the necessary interpreters and compilers for those languages. This allows users to write and run code in various programming languages on their shared hosting accounts.
Explanation of how shared hosting supports different programming languages:
- Interpreted Languages: For interpreted languages like PHP, Python, and JavaScript, the server executes the code directly without the need for compilation. Shared hosting providers typically have pre-installed interpreters for these languages, allowing users to upload and execute their code without any additional setup.
- Compiled Languages: For compiled languages like C, C++, and Java, the code needs to be compiled into machine-readable instructions before being executed. Shared hosting providers may offer compilers for these languages or allow users to install their own compilers.
- Frameworks and Libraries: Shared hosting providers also provide support for popular frameworks and libraries for different programming languages. This includes frameworks like Laravel for PHP, Django for Python, and React for JavaScript.
- Server-Side Configurations: Shared hosting providers configure their servers to support common web development technologies like MySQL databases, Apache web servers, and FTP protocols. This ensures that websites developed using these technologies can function properly on shared hosting platforms.
- Control Panel Integration: Many shared hosting providers integrate programming language support into their control panels. This allows users to manage their code, install plugins, and configure language-specific settings directly through the control panel interface.
- Community Support and Documentation: Shared hosting providers often offer community forums, documentation, and tutorials for various programming languages. This provides users with resources to learn about language-specific features, troubleshoot issues, and find solutions to common problems.
What happens if a website on the same server as mine experiences a security breach?
If a website on the same server as yours experiences a security breach, it can potentially have implications for the overall security and performance of the server, as well as for other websites hosted on the same server. Here are some potential consequences and measures taken in response to a security breach on a shared server:
Isolation Measures:
Hosting providers implement measures to isolate individual accounts on a shared server. This means that the files, databases, and configurations of one website are separated from others. However, the effectiveness of isolation depends on the security measures implemented by the hosting provider.
Immediate Mitigation:
Upon detecting a security breach, hosting providers take immediate steps to mitigate the impact. This may involve isolating the affected account, suspending compromised services, or taking the website offline temporarily.
Security Audits:
Hosting providers conduct security audits to identify the source and extent of the security breach. This involves reviewing server logs, file integrity checks, and other security measures to determine how the breach occurred.
Patch and Update:
If the security breach was due to a known vulnerability in the server software, the hosting provider applies patches and updates to address the issue promptly. Keeping server software up to date is crucial for preventing known vulnerabilities from being exploited.
Client Notifications:
Hosting providers may notify affected clients about the security incident, providing information on the nature of the breach and any actions they need to take. This may include changing passwords, updating website software, or scanning for malware.
Malware Scanning and Removal:
Hosting providers typically run malware scanning tools to identify and remove malicious code from compromised websites. This helps ensure that the server environment is clean and free from threats.
Enhanced Security Measures:
In response to a security breach, hosting providers may enhance security measures across the entire server. This could involve implementing stricter firewall rules, improving intrusion detection systems, and enhancing overall server hardening practices.
Password Resets:
Hosting providers may require affected users to reset their account passwords as a precautionary measure. This helps prevent unauthorized access even if login credentials were compromised during the security breach.
Investigation and Forensics:
Hosting providers conduct investigations and forensics to understand how the security breach occurred and whether it resulted from a specific vulnerability, insecure coding practices, or other factors. This information is crucial for preventing similar incidents in the future.
Communication with Clients:
Hosting providers communicate transparently with their clients, providing updates on the security incident, actions taken, and any additional steps clients need to follow. Clear communication helps build trust and keeps clients informed about the situation.
Can I set up cron jobs on Shared Hosting?
Yes, you can typically set up cron jobs on Shared Hosting. Cron jobs are automated tasks that are scheduled to run at specific times or intervals. They are commonly used for tasks such as:
- Running backups: Cron jobs can be used to automatically back up your website’s files and database on a regular basis.
- Updating software: Cron jobs can be used to automatically update your website’s software, plugins, and themes.
- Sending notifications: Cron jobs can be used to send notifications about website events, such as when a new user registers or when a comment is posted.
- Optimizing your website: Cron jobs can be used to run tasks that optimize your website for performance, such as generating static HTML files or compressing images.
The specific method for setting up cron jobs will vary depending on your hosting provider. However, most providers will have a section in their control panel where you can manage your cron jobs.
What is the policy on upgrading server hardware in Shared Hosting?
The policy on upgrading server hardware in Shared Hosting varies depending on the hosting provider. However, there are some general guidelines that most providers follow.
Hardware Upgrades at the Provider’s Discretion
Shared hosting providers typically upgrade their server hardware on a regular basis to keep up with advances in technology and ensure that their customers have access to the latest hardware. However, they do not always notify their customers when they are planning to upgrade their hardware. This is because the decision of when to upgrade hardware is often made based on a number of factors, such as the age of the hardware, the current demand for resources, and the availability of new hardware.
Upgrades May Require Downtime
In some cases, upgrading server hardware may require downtime. This is because the new hardware may need to be installed and configured before it can be put into service. If a hardware upgrade does require downtime, the hosting provider will typically notify their customers in advance.
Customer Requests for Hardware Upgrades
Most shared hosting providers do not allow customers to request specific hardware upgrades. This is because the hosting provider needs to make sure that all of their customers have access to the same level of resources. However, some providers may offer customers the option to upgrade to a higher-tier shared hosting plan that includes more powerful hardware.
Monitoring Server Performance
It is a good practice to monitor your website’s performance regularly to identify any potential issues. If you find that your website is slow or unresponsive, you can contact your hosting provider to see if there is any problem with the hardware.
Choosing a Reputable Hosting Provider
When choosing a shared hosting provider, it is important to select a reputable company that has a good track record of uptime and performance. You should also make sure that the provider has a clear policy on hardware upgrades.
How does Shared Hosting handle software compatibility for different applications?
Shared hosting providers implement various strategies to ensure compatibility between different applications hosted on their servers.
These strategies include:
Standardized Server Environment: Shared hosting providers typically maintain a standardized server environment that includes pre-installed software components, such as operating systems, web servers, and database management systems. This standardization ensures that applications that are compatible with these components can run smoothly on the shared hosting platform.
Compatibility Testing: Hosting providers often conduct compatibility testing to identify and address potential compatibility issues between different applications. This testing involves installing and running various applications combinations to identify any conflicts or compatibility issues.
Application-Specific Configurations: Shared hosting providers may offer application-specific configurations or modules that allow users to tailor the server environment to specific applications. This customization can help resolve compatibility issues and optimize performance for particular applications.
User Support and Documentation: Hosting providers provide user support and documentation to assist users in troubleshooting compatibility issues and configuring their applications for optimal performance on the shared hosting platform.
Application Versions and Updates: Shared hosting providers typically maintain specific versions of software components and applications to ensure compatibility and stability. They may also offer updates to these components or applications when necessary to address compatibility issues or enhance performance.
Community Forums and Knowledge Bases: Shared hosting providers often maintain online communities and knowledge bases where users can share experiences, seek solutions to compatibility issues, and learn about application-specific configurations.
Integration with Third-Party Tools: Some hosting providers integrate with third-party tools that can scan and analyze applications for potential compatibility issues. These tools can provide valuable insights into compatibility problems and suggest solutions.
Monitoring and Performance Optimization: Shared hosting providers monitor server performance and resource usage to identify potential compatibility issues that may impact performance. They may also implement optimization techniques to ensure that resources are allocated efficiently and applications can operate smoothly.
Can I use a CDN (Content Delivery Network) with Shared Hosting?
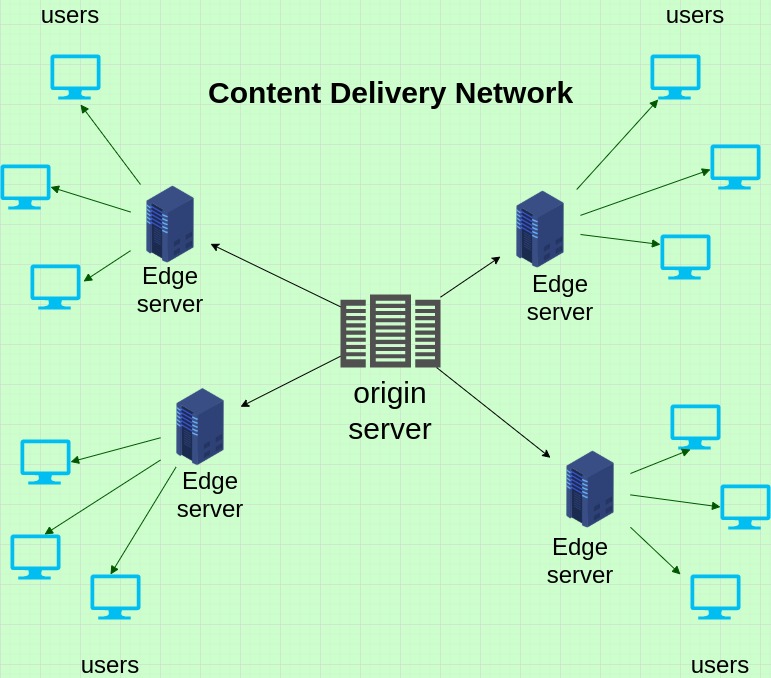
Yes, you can use a CDN (Content Delivery Network) with Shared Hosting. A CDN is a geographically distributed network of servers that delivers content to end users based on their proximity to the nearest server. This can significantly improve website performance by reducing load times and latency.
Many shared hosting providers offer CDN integration as an optional service, or you can set up a CDN independently and configure it to work with your shared hosting account.
Some benefits of using a CDN with shared hosting:
- Improved website performance: CDNs can significantly reduce website load times by caching static content, such as images, CSS, and JavaScript files, closer to end users. This can improve the user experience and make your website more responsive.
- Reduced bandwidth consumption: CDNs can help to reduce bandwidth consumption for your shared hosting account, which can save you money on your hosting costs.
- Global reach: CDNs have servers located all over the world, so they can deliver your content to users in any location. This can be especially beneficial if your website has a global audience.
- Increased availability: CDNs can help to protect your website from outages by providing redundancy. If one server goes down, your content can still be delivered from other servers in the network.
What is the process for scaling resources during traffic growth on Shared Hosting?
Shared Hosting plans may have limitations on resource scaling. Discuss with your hosting provider the process and options available for scaling resources if your website experiences significant growth.
The process for scaling resources during traffic growth on Shared Hosting typically involves the following steps:
Monitoring Traffic and Resource Usage: Continuously monitor website traffic and resource usage patterns to identify trends and potential bottlenecks. This can be done using tools provided by the hosting provider or external monitoring services.
Identifying Resource Needs: Analyze the collected data to determine which resources are being used most heavily and whether they are reaching their limits. This may involve CPU usage, RAM consumption, disk space utilization, or network bandwidth.
Planning for Scalability: Based on the identified resource needs, plan for the necessary scaling measures. This may involve upgrading the shared hosting plan to a higher tier with more resources, such as more CPU cores, more RAM, or more disk space.
Communicating with the Hosting Provider: Contact the hosting provider and discuss the scalability plan. They can provide guidance on available upgrade options, pricing, and potential downtime during the upgrade process.
Scheduling the Upgrade: Schedule the upgrade during a period of low website traffic to minimize disruption to users. The hosting provider will handle the technical aspects of the upgrade, including installing new hardware or configuring server settings.
Monitoring Performance After Upgrade: Once the upgrade is complete, closely monitor website performance and resource usage to ensure that the upgraded resources are sufficient to handle the traffic growth.
Continuous Evaluation and Optimization: Regularly evaluate website performance and resource usage to determine if further scaling measures are necessary. This proactive approach helps maintain optimal performance and avoid potential bottlenecks.
How does Shared Hosting handle software licensing for applications and scripts?
Shared Hosting providers often manage software licensing for server-side applications. Confirm with your provider to ensure compliance with licensing agreements for any specific applications you intend to use.
Shared hosting providers typically handle software licensing for applications and scripts in two ways:
- Bundled with Hosting Plans: Some shared hosting providers bundle popular open-source applications or scripts with their hosting plans. This means that you can install and use these applications without having to purchase separate licenses. For example, many shared hosting providers bundle WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal CMS platforms with their plans.
- Third-Party Licensing: For applications and scripts that are not bundled with the hosting plan, shared hosting providers generally allow you to install and use them if you have a valid license. This means that you will need to purchase a license directly from the application or script developer before using it on your shared hosting account.
Verification of Licenses
Shared hosting providers may verify that you have a valid license for applications or scripts installed on your account. This verification process may involve asking you to provide proof of purchase or checking for a valid license key. If you are unable to provide proof of a valid license, the hosting provider may ask you to remove the application or script from your account.
Responsibility for Licensing
Ultimately, you are responsible for ensuring that you have a valid license for any software applications or scripts you install on your shared hosting account. Failure to comply with licensing terms may result in legal consequences.
Recommendations
To avoid any issues with software licensing on shared hosting, it is recommended to:
- Use bundled applications or scripts: Whenever possible, choose applications or scripts that are bundled with your shared hosting plan to avoid the need for separate licensing.
- Verify license requirements: Before installing any third-party applications or scripts, check the developer’s website or contact them directly to determine the licensing requirements.
- Keep license documentation: Maintain records of your software licenses, including purchase receipts or license keys, in case the hosting provider requests verification.
Can I transfer my existing website from another hosting provider to a Shared Hosting plan seamlessly?
Most hosting providers offer website migration assistance. However, the process can vary, so it’s recommended to inquire about the specific steps and support available for transferring your website.
Transferring your existing website from another hosting provider to a Shared Hosting plan can be a straightforward process, but there are a few steps involved to ensure a seamless transfer.
General outline of the process:
Choose a Shared Hosting Provider: Select a reputable shared hosting provider that offers the necessary features, resources, and support for your website. Consider factors such as uptime, performance, customer support, and compatibility with your website’s software.
Back up your website: Before making any changes to your website’s hosting, it’s crucial to create a complete backup of your website’s files and database. This backup can be used to restore your website if something goes wrong during the transfer process.
Export your website’s database: If your website uses a database (such as MySQL or PostgreSQL), you’ll need to export the database from your current hosting provider. This can usually be done through the provider’s control panel or using database management tools.
Sign up for a Shared Hosting plan: Once you’ve chosen a shared hosting provider, sign up for a plan that meets your website’s needs. You’ll typically need to provide your domain name and payment information.
Create a new database on the Shared Hosting plan: In the Shared Hosting provider’s control panel, create a new database for your website. This database will be where you’ll import your exported database from the previous hosting provider.
Upload website files to the Shared Hosting plan: Upload your website’s files to the Shared Hosting provider’s server. This can usually be done using FTP or a file transfer tool provided by the hosting provider.
Import your database into the Shared Hosting plan: Import the exported database from your previous hosting provider into the new database you created on the Shared Hosting plan. This can be done using database management tools or through the Shared Hosting provider’s control panel.
Update website configuration: If necessary, update your website’s configuration files to reflect the new hosting environment. This may involve changing database connection details, file paths, or URLs.
Test your website: Once the website files and database have been transferred and configuration updates have been made, thoroughly test your website to ensure it’s functioning correctly. This includes checking all pages, links, forms, and database-driven features.
Point your domain name to the Shared Hosting plan: Update your domain name’s DNS records to point to the new Shared Hosting provider’s servers. This will direct visitors to your website to the new hosting environment.
Monitor website performance: After the transfer is complete, monitor your website’s performance and resource usage to ensure it’s operating smoothly on the Shared Hosting plan. Address any issues that may arise promptly.
What is VPS hosting?
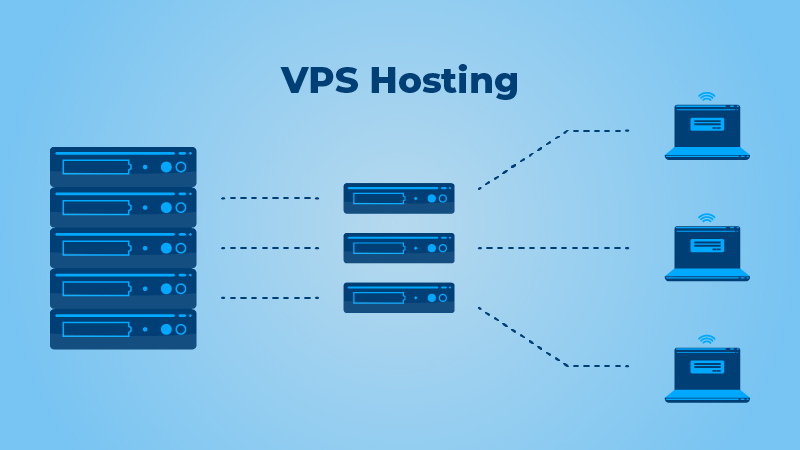
VPS hosting is a more expensive type of web hosting than shared hosting. This is because you have your own virtual private server (VPS). This means that you are still sharing a physical server with other websites, but you have your own dedicated resources. This can improve performance and reliability. VPS hosting is a good option for websites that are experiencing some growth or that require more resources than shared hosting can provide.
VPS hosting is an excellent choice for users who require more control, customization, and dedicated resources than shared hosting can provide, without the cost of a dedicated server. It offers a balance between affordability and performance, making it a popular choice for a wide range of websites and applications.
VPS hosting, which stands for Virtual Private Server hosting, is a type of web hosting that provides a virtual machine (VM) environment on a physical server. This means that you have your own dedicated resources, such as CPU, RAM, and storage, that are not shared with other websites hosted on the same server. This makes VPS hosting a more powerful and flexible option than shared hosting, but it is also more expensive.
Virtual Private Server (VPS) web hosting stands out as a highly favored hosting solution, primarily due to its optimal blend of cost-effectiveness and professional-grade functionality. The term VPS, short for Virtual Private Server, characterizes the configuration of a web server. Web servers, essentially robust computers, play the crucial role of delivering information to web pages, facilitating global access for visitors. Each time a visitor accesses one of your web pages, they are essentially retrieving content directly from your dedicated section of the web server.
In essence, a virtual private server represents a dedicated segment within a web server exclusively allocated to host your website. VPS hosting essentially merges the advantages of shared hosting, known for its cost efficiency, with those of dedicated hosting, recognized as the most potent form of web hosting. It’s not uncommon for individuals to draw parallels between shared hosting and VPS hosting, as both involve partitioning a server to cater to multiple hosting plans. However, it’s crucial to note that, unlike shared web hosting, VPS hosting doesn’t impose any constraints or limitations on the types of software that can be utilized on the allocated web server partition
What is the features of VPS hosting?

VPS hosting, or Virtual Private Server hosting, is a type of web hosting that falls between shared hosting and dedicated hosting. With VPS hosting, you share a physical server with other users, but your virtual server is isolated from the others, meaning that you have more control over your resources and security.
Features of VPS hosting:
- Root access: With VPS hosting, you have root access to your virtual server, which means that you can install any software you want and configure the server to your specific needs. This gives you a lot of flexibility and control over your hosting environment.
- Isolated environment: Each virtual server on a VPS hosting plan is isolated from the others, meaning that you don’t have to worry about your website’s performance being affected by other users on the server. This can be a major advantage for websites that experience high traffic or require consistent performance.
- Scalability: VPS hosting is a very scalable solution. You can start with a small plan and then upgrade to a larger plan as your needs grow. This makes it a good option for businesses that are expecting to grow in the future.
- Multiple operating systems: VPS hosting providers typically offer a variety of operating systems to choose from, including Linux and Windows. This gives you the flexibility to choose the operating system that best suits your needs.
- Security: VPS hosting is generally more secure than shared hosting, as your virtual server is isolated from the others. This means that you are less likely to be affected by security breaches that may occur on other websites on the server.
- Customer support: VPS hosting providers typically offer 24/7 customer support, which can be helpful if you need assistance with managing your server or if you encounter any problems.
- Cost-effective: VPS hosting is a more cost-effective option than dedicated hosting, but it still offers a lot of the same benefits. This makes it a good option for businesses that need more control over their hosting environment but don’t have the budget for a dedicated server.
VPS hosting is a good option for businesses that are looking for a hosting solution that offers more flexibility, control, and security than shared hosting. It is also a good option for businesses that are expecting to grow in the future, as it is a very scalable solution.
Who benefits from VPS hosting?
VPS hosting caters to the requirements of small to medium-sized enterprises seeking the capabilities of a dedicated server without incurring additional costs or assuming server maintenance responsibilities. If you’ve been experiencing diminished site performance and downtime with a shared hosting plan, transitioning to a VPS hosting plan may be necessary.
Individuals seeking absolute control over their server’s software configuration and control panel find VPS hosting ideal. In contrast to shared hosting, where you’re bound by the hosting company’s mandated software configuration, VPS offers a private web server experience without the high setup and maintenance expenses.
Websites undergoing expansion and requiring more power than a shared hosting plan provides find VPS hosting to be the perfect solution. While many webmasters initially opt for shared hosting due to its affordability and simplicity, as their sites attract increasing daily traffic, the strain on a single shared hosting account becomes overwhelming. VPS hosting stands out as the most adaptable hosting option, boasting a wide array of plans to meet diverse needs.
With some hosting companies offering up to 10 VPS hosting plans ranging from $10 to $300, it’s evident why sites of various sizes are turning to VPS hosting to fulfill their web hosting requirements.
What are the benefits of opting for VPS hosting?
A key advantage of VPS hosting lies in the flexibility it offers in terms of hosting plans. Unlike being restricted to a fixed set of server resources, you have the option to scale your plan as needed, typically at any time. If you find yourself uncertain about the amount of server resources required to ensure optimal performance for your websites, you might want to explore robust VPS plans or consider a cloud VPS hosting option.
Remarkably, VPS web hosting tends to be cost-effective in many instances, with pricing starting slightly above that of shared web hosting. This combination of affordability and scalability renders VPS web hosting ideal for both novice webmasters and seasoned professionals. The process of upgrading a VPS hosting plan is remarkably straightforward, particularly if you opt to stick with the same hosting provider.
Benefits of VPS hosting:
Enhanced Performance: VPS hosting provides dedicated resources, including CPU, RAM, and storage, ensuring consistent performance even during peak traffic periods. This is in contrast to shared hosting, where resources are shared among multiple users, leading to potential performance slowdowns.
- Greater Control: VPS hosting grants root access to the virtual server, allowing for complete customization and configuration to meet specific needs. This includes the ability to install preferred software, modify server settings, and optimize performance for specific applications.
- Improved Security: VPS hosting isolates each virtual server from others on the physical server, preventing resource contention and reducing the risk of security breaches. This isolation also means that security issues on one virtual server won’t affect others, enhancing overall security.
- Scalability: VPS hosting is highly scalable, allowing for easy upgrades to accommodate growing resource demands. As traffic or storage requirements increase, users can seamlessly upgrade their VPS plan without downtime or major disruptions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: VPS hosting offers a balance between shared hosting’s affordability and dedicated hosting’s high cost. It provides dedicated resources and control at a more economical price point, making it an attractive option for businesses with moderate resource requirements.
- Versatility: VPS hosting supports a wide range of applications and operating systems, making it suitable for various websites and projects. This flexibility allows users to choose the environment that best suits their specific needs.
- Reliability: VPS hosting typically provides higher uptime and reliability compared to shared hosting due to its dedicated resources and isolation. This ensures that websites and applications remain accessible and perform consistently for users.
- Reduced Maintenance: VPS hosting providers often offer managed VPS plans, where the hosting company handles server maintenance and technical support, allowing users to focus on their core business activities.
- Flexibility for Developers: VPS hosting provides a flexible environment for developers to test and deploy applications, experiment with different configurations, and gain valuable experience in server administration.
- Ideal for Growth: VPS hosting is well-suited for businesses that anticipate growth in their website traffic or resource demands. The scalability of VPS allows them to accommodate increasing requirements without the need for major infrastructure changes.
What is the cost of VPS hosting?
Typically, VPS hosting providers present a variety of scalable plans, allowing users to adjust the size of their allocated server partition based on their website’s requirements. Given that a VPS is essentially a segmented portion of a web server, hosting providers commonly offer multiple VPS plans.
For instance, major hosting companies may provide as many as nine distinct levels of VPS hosting, resulting in a wide range of prices. While the cost can vary significantly due to this diverse plan selection, most companies generally offer plans priced between $20 and $200 per month.
It’s crucial to recognize that the realm of VPS hosting encompasses a broad spectrum of offerings, and pricing is not the sole determinant when selecting a plan. Instead, it is advisable to focus on understanding and meeting your specific needs as a webmaster.
What exactly is Cloud VPS hosting?
Cloud VPS hosting stands in contrast to traditional VPS hosting, which operates outside of the cloud environment. The distinctions between the capabilities and constraints of Cloud VPS hosting and its conventional counterpart are quite pronounced. Conventional VPS hosting adheres to strict limitations set by the provider to maintain optimal web server performance.
In a refreshing departure from these constraints, Cloud VPS hosting does not impose such rigid boundaries. This is made possible by the simultaneous connection to various servers within the network. Unlike conventional VPS hosting, cloud hosting plans operate on a pay-as-you-go model. Essentially, users have unrestricted access to server resources, and any usage beyond the predefined limits results in charges for the additional resources consumed by their websites. Opting for VPS cloud hosting becomes particularly advantageous when anticipating fluctuating levels of site traffic or expecting substantial surges in web visits.
How does the functionality of Cloud VPS hosting differ?
Cloud VPS hosting sets itself apart from conventional web hosting by leveraging a network of web servers operating collaboratively to furnish server resources concurrently to numerous websites. While it may seem akin to VPS hosting, it distinguishes itself through the absence of constraints on the allocation of resources to a specific website at any given moment. Prominent entities on the internet, including Google, Yahoo, Bing, Amazon, and other sizable corporate sites, harness the capabilities of cloud hosting to efficiently transmit data. Opting for cloud VPS hosting is advisable if you seek the swiftest web hosting solution for your site, as it offers unparalleled speed and resource flexibility.
Can I upgrade my VPS hosting plan?
Yes, in most cases, you can upgrade your VPS hosting plan. VPS hosting providers typically offer scalable plans to accommodate the evolving needs of your website or application. Upgrading your VPS hosting plan allows you to access additional resources such as more CPU power, RAM, storage, and bandwidth.
- Identify Your Needs: Determine the resources you require, such as CPU cores, RAM, storage, and bandwidth. Analyze your current usage patterns and project future demands to select an appropriate plan.
- Choose a Hosting Provider: Consider factors like reputation, customer support, pricing, and features when selecting a hosting provider. Review their upgrade policies and procedures to ensure a smooth transition.
- Select an Upgrade Plan: Compare different plan options offered by your hosting provider. Ensure the upgraded plan meets your resource requirements and aligns with your budget.
- Initiate the Upgrade Process: Contact your hosting provider’s support team to initiate the upgrade process. They will guide you through the necessary steps and provide technical assistance if needed.
- Data Transfer (Optional): If you have a significant amount of data, you may need to transfer it to the new VPS server. The hosting provider may offer migration tools or services to assist with this process.
- Configuration and Testing: Once the upgrade is complete, configure the new VPS server and test your website or application to ensure it functions properly.
- DNS Updates (Optional): If you have made any changes to your domain name or DNS settings, propagate those changes to ensure your website remains accessible to users.
What operating systems can I use with VPS hosting?

VPS hosting providers typically offer a variety of operating systems to cater to the diverse needs and preferences of their users. The specific operating systems available may depend on the hosting provider, but some of the common options include:
Linux Distributions:
- Ubuntu
- CentOS
- Debian
- Fedora
- Arch Linux
- openSUSE
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)
- and more
Windows Server Editions:
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2019
BSD (Berkeley Software Distribution) Variants:
- FreeBSD
- OpenBSD
Other Operating Systems:
- CentOS Stream
- AlmaLinux
- Oracle Linux
- CoreOS
- VMware ESXi (for virtualization purposes)
When choosing an operating system for your VPS, consider factors such as your familiarity with the OS, compatibility with the applications you intend to run, and any specific features or security considerations you may require.
Linux distributions are a popular choice for VPS hosting due to their stability, security, and the wide range of open-source software available. They also often come with lower licensing costs compared to Windows Server editions.
Windows Server editions are suitable for users who require specific Windows-based applications or environments. These editions provide compatibility with technologies like ASP.NET, Microsoft SQL Server, and other Windows-specific services.
Before selecting an operating system for your VPS, it’s recommended to check with your hosting provider to ensure they offer the OS you prefer. Additionally, some providers may allow you to upload and install custom operating system images if their standard offerings do not meet your requirements.
What are the typical use cases for VPS hosting?
VPS hosting is a versatile solution that can be used for a wide range of purposes.
The typical use cases for VPS hosting:
- Hosting medium to high-traffic websites: VPS hosting can handle the increased traffic and resource demands of medium to high-traffic websites, ensuring consistent performance and stability.
- Running resource-intensive applications: VPS hosting provides dedicated resources, including CPU, RAM, and storage, making it suitable for running resource-intensive applications like video streaming, data processing, and complex web applications.
- Developing and testing web applications: VPS hosting offers a flexible and isolated environment for developers to test and deploy web applications without affecting live production environments.
- Hosting e-commerce websites: VPS hosting provides the security and performance required for e-commerce websites, ensuring secure transactions and a seamless shopping experience for customers.
- Setting up game servers: VPS hosting offers the dedicated resources and low latency required for hosting game servers, providing a smooth gaming experience for players.
- Running VPN servers: VPS hosting is a popular choice for setting up VPN servers, allowing users to securely access private networks and protect their online privacy.
- Hosting email servers: VPS hosting provides the scalability and reliability required for hosting email servers, ensuring efficient email delivery and storage.
- Running CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems: VPS hosting can handle the data storage and processing requirements of CRM systems, enabling businesses to manage customer relationships effectively.
- Hosting file-sharing servers: VPS hosting can store and share large files securely and efficiently, making it a suitable solution for file-sharing services.
- Running cryptocurrency mining software: VPS hosting provides the dedicated resources and power required for cryptocurrency mining operations.
VPS hosting is a versatile and powerful solution that can be used for a wide range of purposes, from hosting websites and applications to running resource-intensive tasks and providing specialized services. Its scalability, performance, and control make it a popular choice for businesses and individuals seeking a reliable and flexible hosting environment.
Is there a difference between managed and unmanaged VPS hosting?
Yes, there is a significant difference between managed and unmanaged VPS hosting. The primary distinction lies in the level of support and maintenance provided by the hosting provider.
Managed VPS hosting offers comprehensive support and maintenance, taking care of all server-related tasks such as:
- Operating system installation and configuration
- Software updates and security patches
- Server monitoring and performance optimization
- Troubleshooting and technical assistance
- Backup and disaster recovery
This hands-off approach allows users to focus on their core business activities without worrying about the technical intricacies of server management. Managed VPS hosting is ideal for businesses that lack the technical expertise or time to manage their own servers.
Unmanaged VPS hosting, on the other hand, provides the server infrastructure and resources but leaves the management entirely to the user.
This means that users are responsible for:
- Installing and configuring the operating system
- Keeping software up to date and applying security patches
- Monitoring server performance and addressing any issues
- Troubleshooting technical problems
- Implementing backup and disaster recovery solutions
Unmanaged VPS hosting is a cost-effective option for users with technical expertise who are comfortable managing their own servers. It offers greater control over the server environment but requires a significant investment of time and effort.
| Feature | Managed VPS Hosting | Unmanaged VPS Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Support level | Comprehensive | Limited |
| Maintenance | Handled by the hosting provider | Managed by the user |
| Technical expertise | Not required | Required |
| Control | Less control | Full control |
| Cost | More expensive | Less expensive |
| Target audience | Businesses, individuals without technical expertise | Technical users, developers, system administrators |
Can I install custom software on my VPS?
Yes, you can typically install custom software on your VPS. VPS hosting provides you with root access to your server, which means that you have the ability to install any software that you want. This can be a major advantage over shared hosting, as it allows you to customize your server environment to meet your specific needs.
Benefits of installing custom software on your VPS:
- Tailored to your needs: You can install software that is specifically designed for your business or applications.
- Enhanced functionality: You can add features and functionality that are not available with pre-installed software.
- Improved performance: You can optimize software for your specific hardware and operating system.
- Greater security: You can install security patches and updates as soon as they are released.
- Reduced costs: You may be able to save money by installing open-source software or by purchasing software licenses directly from the vendor.
Of course, there are also some potential drawbacks to installing custom software on your VPS:
- Increased complexity: Managing custom software can be more complex than managing pre-installed software.
- Security risks: Installing software from untrusted sources can pose security risks.
- Compatibility issues: Custom software may not be compatible with your operating system or hardware.
- Troubleshooting challenges: Troubleshooting custom software can be more difficult, especially if you don’t have the necessary expertise.
The decision of whether or not to install custom software on your VPS is a trade-off between flexibility and control on the one hand, and ease of use and security on the other. If you have the technical expertise and are willing to take on the additional responsibility, then installing custom software can be a great way to tailor your VPS to your specific needs. However, if you are not comfortable managing custom software, then you may be better off sticking with pre-installed software or using a managed VPS hosting service that handles software installation and maintenance for you.
How does VPS hosting impact website performance?

VPS hosting can significantly impact website performance by providing dedicated resources, improved security, and enhanced scalability.
Explanation of how VPS hosting contributes to better website performance:
- Dedicated Resources: VPS hosting allocates dedicated resources, including CPU, RAM, and storage, solely to your website. This eliminates the resource contention that occurs in shared hosting, where multiple websites share the same physical server. With dedicated resources, your website has preferential access to processing power, memory, and storage, ensuring consistent performance even during peak traffic periods.
- Improved Security: VPS hosting isolates your website from other websites on the same physical server. This isolation prevents resource-intensive or insecure websites from affecting your website’s performance or security. Additionally, VPS hosting allows you to install your own security software and firewalls, further enhancing the protection of your website and its data.
- Enhanced Scalability: VPS hosting is highly scalable, allowing you to easily upgrade your resources as your website’s traffic and storage demands grow. If your website experiences a sudden surge in traffic, you can quickly upgrade your VPS plan to accommodate the increased demand without downtime or performance bottlenecks. This flexibility ensures that your website can handle growing traffic without compromising performance.
- Root Access and Customization: VPS hosting grants you root access to your server, giving you complete control over the server environment. You can install any software you need, customize configurations, and optimize the server for your specific website requirements. This level of control allows you to tailor your VPS to your website’s unique needs and maximize its performance potential.
- Reduced Latency and Faster Response Times: VPS hosting often provides lower latency and faster response times compared to shared hosting. This is because your website has a direct connection to the physical server, eliminating the need to share resources with other websites. Lower latency translates to quicker page load times, smoother user interactions, and an overall improved browsing experience.
VPS hosting offers a significant boost to website performance by providing dedicated resources, enhanced security, scalability, root access, and reduced latency. By choosing VPS hosting, you can ensure that your website can handle growing traffic, maintain consistent performance, and provide a seamless user experience.
What is the role of the control panel in VPS hosting?
A control panel is an essential component of VPS hosting, providing a user-friendly interface for managing and administering the server. It serves as a centralized hub for performing various tasks related to website management, server configuration, and account administration.
Key roles of a control panel in VPS hosting:
1. Website Management:
- Upload and manage website files
- Create and manage databases
- Configure email accounts
- Set up FTP access
- Install and manage web applications
2. Server Configuration:
- Manage network settings
- Configure firewalls and security settings
- Monitor server performance and resource usage
- Install and update software
- Schedule backups and recovery procedures
3. Account Administration:
- Create and manage user accounts
- Assign permissions and access controls
- Set up billing and payment options
- Manage customer support tickets
- Monitor resource usage and bandwidth quotas
The control panel simplifies these tasks, making it easier for users to manage their VPS hosting environment without requiring in-depth technical knowledge. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that abstracts away the complexities of server administration, allowing users to perform common tasks with just a few clicks.
These core functions, many control panels offer advanced features such as:
- Website analytics and traffic monitoring
- Spam filtering and email protection
- Search engine optimization (SEO) tools
- Application deployment and management
- Cloud storage integration
The specific features and functionality of a control panel vary depending on the provider and the chosen plan. However, the general purpose remains the same: to provide a user-friendly and intuitive interface for managing and administering VPS hosting environments.
A control panel plays a crucial role in VPS hosting by bridging the gap between technical complexity and user-friendliness. It empowers users, regardless of their technical expertise, to effectively manage their VPS hosting environment, ensuring optimal performance, security, and ease of use.
Is VPS hosting suitable for beginners?
VPS hosting can be a suitable option for beginners, but it depends on their technical skills and comfort level with server administration. For those with some technical expertise and a willingness to learn, VPS hosting offers a balance of flexibility, control, and affordability compared to shared hosting.
Breakdown of the suitability of VPS hosting for beginners:
Pros:
- More control and flexibility: VPS hosting grants root access to the server, allowing beginners to learn and experiment with server configurations and software installation.
- Dedicated resources: VPS hosting provides dedicated CPU, RAM, and storage, ensuring consistent performance even during traffic spikes.
- Scalability: VPS hosting can be easily upgraded as traffic or resource demands grow.
- Security: VPS hosting isolates the user’s server from others, reducing security risks.
Cons:
- Technical complexity: VPS hosting requires some technical knowledge to manage and maintain.
- Troubleshooting challenges: Troubleshooting issues on a VPS may require more technical expertise compared to shared hosting.
- Limited support: Unmanaged VPS plans often provide limited support, requiring users to resolve issues themselves.
For beginners with limited technical experience, managed VPS hosting plans can be a viable option. Managed VPS hosting providers handle server maintenance, software updates, and technical support, allowing beginners to focus on their website or applications without worrying about server administration.
Can I upgrade my VPS hosting plan without downtime?
Yes, it is possible to upgrade your VPS hosting plan without downtime in most cases. This is because most hosting providers use technology that allows them to seamlessly transition your server to the new plan without interrupting your website or application.
Steps that are typically involved in upgrading your VPS hosting plan without downtime:
- Choose the new plan: Select the new VPS hosting plan that meets your increased resource requirements.
- Notify your hosting provider: Inform your hosting provider about your intention to upgrade and request a downtime-free migration.
- Schedule the upgrade: Coordinate with your hosting provider to schedule a time for the upgrade to take place.
- Initiate the upgrade process: The hosting provider will initiate the upgrade process, which may involve provisioning new resources, configuring the server, and transferring data.
- Monitor the upgrade: Keep an eye on the upgrade process and communicate with your hosting provider if any issues arise.
- Confirm the upgrade: Once the upgrade is complete, verify that your website or application is functioning correctly on the new plan.
To minimize the risk of downtime during the upgrade process, hosting providers often utilize technologies such as live migration, which involves transferring the server’s data and processes to the new hardware without interrupting service. This technology allows for a seamless transition to the new plan, ensuring that your website or application remains accessible to users throughout the process.
If you are concerned about downtime during the upgrade, you can discuss your concerns with your hosting provider. They can provide more specific details about their upgrade process and the measures they take to minimize downtime. By working closely with your hosting provider, you can ensure a smooth and seamless transition to your new VPS hosting plan without disrupting your website or application.
Can I backup my VPS data?
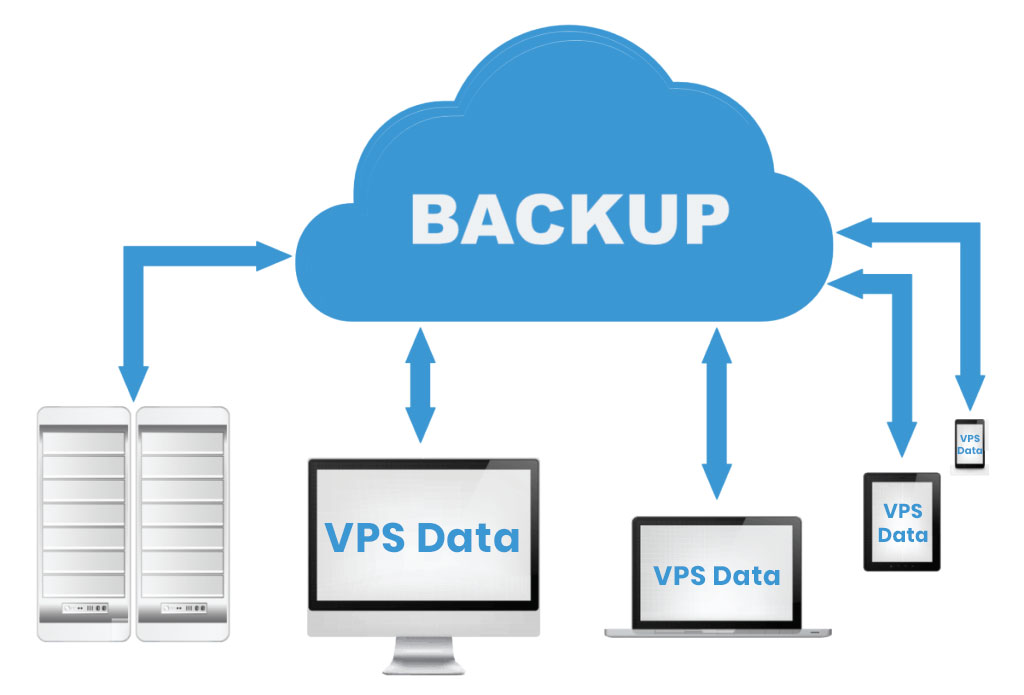
Yes, it is essential to back up your VPS data regularly to protect against data loss due to hardware failures, software glitches, cyberattacks, or human errors. Backing up your data ensures that you have a copy of your website’s files, databases, and other critical information, allowing you to restore your site in case of data loss.
There are several methods for backing up your VPS data, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Some common methods:
1. Full Server Backup:
A full server backup creates an exact copy of your entire VPS, including the operating system, software, configuration files, and all user data. This type of backup provides the most comprehensive protection but can be time-consuming and require significant storage space.
2. System State Backup:
A system state backup creates a copy of the operating system’s configuration and critical files. This type of backup is smaller than a full server backup and can be restored more quickly, but it does not include all user data.
3. File-Level Backup:
A file-level backup selectively backs up specific files or directories, such as website files, databases, or email archives. This type of backup offers flexibility and control over which data is backed up but requires more manual effort to manage.
4. Scheduled Backups:
Scheduled backups automate the backup process, ensuring that your data is backed up regularly without manual intervention. This method is highly recommended to maintain data integrity and protection.
5. Cloud Backup Services:
Cloud backup services provide offsite storage for your backups, offering additional protection against local hardware failures or disasters. These services typically charge recurring fees for storage and bandwidth usage.
The specific backup method you choose will depend on your needs, preferences, and the amount of data you need to protect. It’s advisable to consult with your hosting provider or a data backup specialist to determine the best backup strategy for your VPS environment.
Is VPS hosting suitable for high-traffic websites?
Yes, VPS hosting is a suitable option for high-traffic websites due to its ability to provide dedicated resources, scalability, and performance.
Explanation of why VPS hosting is well-suited for handling high traffic:
- Dedicated Resources: VPS hosting allocates dedicated CPU, RAM, and storage to your website, ensuring that it has the necessary resources to handle increased traffic without compromising performance. Unlike shared hosting, where resources are shared among multiple websites, VPS hosting prevents resource contention and ensures consistent performance even during peak traffic periods.
- Scalability: VPS hosting is highly scalable, allowing you to easily upgrade your resources to accommodate growing traffic demands. If your website experiences a sudden surge in traffic, you can quickly upgrade your VPS plan to provide more CPU, RAM, or storage without downtime or performance bottlenecks. This flexibility ensures that your website can handle growing traffic without compromising performance or user experience.
- Isolation and Security: VPS hosting isolates your website from other websites on the same physical server. This isolation prevents resource-intensive or insecure websites from affecting your website’s performance or security. Additionally, VPS hosting allows you to install your own security software and firewalls, further enhancing the protection of your website and its data.
- Enhanced Performance: VPS hosting provides a dedicated environment for your website, allowing you to optimize the server configuration and software settings specifically for your website’s needs. This level of control can significantly improve performance and ensure that your website can handle high traffic without slowing down or experiencing issues.
- Cost-Effectiveness: VPS hosting offers a balance between shared hosting’s affordability and dedicated hosting’s high cost. It provides dedicated resources and scalability at a more economical price point, making it a suitable option for businesses with high-traffic websites that require consistent performance and control over their hosting environment.
VPS hosting offers a powerful and flexible solution for high-traffic websites. Its dedicated resources, scalability, performance, and security make it an ideal choice for businesses that need to ensure their websites can handle growing traffic and maintain a seamless user experience.
What is the difference between SSD and HDD storage in VPS hosting?
SSD (Solid State Drive) and HDD (Hard Disk Drive) are two types of storage devices used in VPS hosting. They differ significantly in their technology, performance, and cost.
SSD Storage
SSD storage uses NAND flash memory to store data. This makes it faster and more reliable than HDD storage, as there are no moving parts to break down. SSDs also offer lower latency, which means that your website will load faster and respond more quickly to user requests.
HDD Storage
HDD storage uses spinning magnetic platters to store data. This makes it slower and less reliable than SSD storage, as the platters can wear out over time and the drive can be damaged if it is dropped or shaken. HDDs also have higher latency, which can cause your website to load slower and respond less quickly to user requests.
Differences between SSD and HDD storage in VPS hosting
| Feature | SSD Storage | HDD Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | NAND flash memory | Spinning magnetic platters |
| Performance | Faster | Slower |
| Reliability | More reliable | Less reliable |
| Latency | Lower | Higher |
| Cost | More expensive | Less expensive |
In general, SSD storage is the better choice for VPS hosting, as it offers faster performance, higher reliability, and lower latency. However, HDD storage is still a viable option for businesses that are on a tight budget or that do not require the highest level of performance.
Can I use VPS hosting for development and testing purposes?
Yes, VPS hosting is a suitable option for development and testing purposes. Its dedicated resources, scalability, and flexibility make it an ideal platform for creating and refining your applications before deploying them to a production environment.
Benefits of using VPS hosting for development and testing:
1. Dedicated Resources: VPS hosting provides dedicated CPU, RAM, and storage, ensuring that your development and testing environment has the resources it needs to perform smoothly. This prevents resource contention and ensures consistent performance, even when running multiple development tools or testing scenarios simultaneously.
2. Scalability: VPS hosting is highly scalable, allowing you to easily upgrade or downgrade your resources as your development needs change. If your project requires more resources, you can quickly upgrade your VPS plan to accommodate the increased demand. Conversely, if your project is in its early stages and doesn’t require extensive resources, you can choose a more affordable plan and scale up as needed.
3. Isolation and Security: VPS hosting isolates your development environment from other websites or applications on the same physical server. This isolation prevents potential conflicts or interference from other users and ensures that your development environment remains secure. Additionally, VPS hosting allows you to implement your own security measures, such as firewalls and access controls, to further protect your development work.
4. Flexibility and Control: VPS hosting grants you root access to your server, providing complete control over the environment. You can install any software or development tools you need, customize configurations, and optimize the server for your specific project requirements. This level of control allows you to tailor your VPS to your development workflow and preferences.
5. Cost-Effectiveness: VPS hosting offers a balance between shared hosting’s affordability and dedicated hosting’s high cost. It provides dedicated resources and scalability at a more economical price point, making it a cost-effective solution for development and testing purposes.
How does VPS hosting contribute to website scalability?

VPS hosting contributes to website scalability by providing a flexible and scalable infrastructure that allows users to easily adjust their resources as needed.
Some ways in which VPS hosting supports website scalability:
Resource Allocation:
VPS hosting allocates dedicated resources to each virtual server. These resources typically include CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth. As the website’s needs grow, users can easily scale up by increasing these allocated resources.
Scalable Plans:
VPS hosting plans are often designed to be scalable. Hosting providers offer different plans with varying levels of resources, allowing users to choose a plan that matches their current requirements. Additionally, users can upgrade their plans as their website traffic and resource demands increase.
Customizable Configuration:
VPS hosting allows users to customize the configuration of their virtual server. This includes the ability to install and configure software, choose the operating system, and adjust server settings. This customization facilitates the adaptation of the server environment to specific scalability requirements.
Easy Resource Upgrades:
When a website experiences increased traffic or requires more computing power, users can easily upgrade their VPS hosting plan to access additional resources. This can typically be done through the hosting provider’s control panel or customer portal without significant downtime.
Traffic Handling:
VPS hosting provides a dedicated and isolated environment for each virtual server. This means that the performance of one VPS is not directly affected by the activities of other virtual servers on the same physical machine. This isolation contributes to more predictable and scalable performance.
Load Balancing:
For websites with fluctuating traffic patterns, load balancing can be implemented with VPS hosting. Load balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple VPS instances, ensuring efficient use of resources and improved scalability to handle varying loads.
Instant Provisioning:
VPS hosting typically offers rapid provisioning of resources. Users can quickly add more CPU, RAM, or storage to their virtual server without the delays associated with traditional server provisioning.
Snapshot and Cloning:
Some VPS hosting providers offer features like server snapshots and cloning. Snapshots allow users to capture a point-in-time image of their server configuration, while cloning enables the creation of identical copies of a server. These features simplify the process of scaling by providing a baseline configuration that can be replicated.
Vertical and Horizontal Scaling:
VPS hosting supports both vertical and horizontal scaling. Vertical scaling involves increasing the resources (CPU, RAM) of the existing server, while horizontal scaling involves adding more servers to distribute the load. VPS hosting allows users to choose the most appropriate scaling strategy for their specific needs.
Developer-Friendly Environment:
VPS hosting is developer-friendly, allowing users to install and configure custom applications and software. This flexibility enables developers to optimize the website’s architecture for scalability.
VPS hosting facilitates website scalability by providing a foundation for resource allocation, easy upgrades, and customization. Users can adapt their hosting environment to match the changing demands of their websites, ensuring optimal performance and responsiveness as traffic and resource requirements evolve.






